Figure 1.
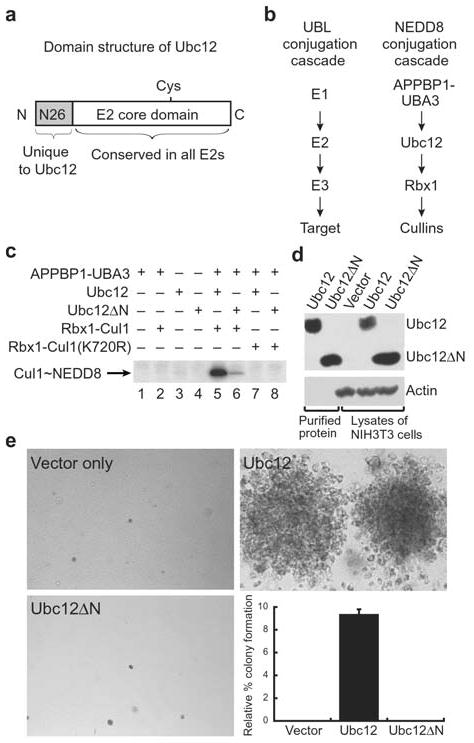
Ubc12’s N-terminal extension is important for function. a, Domain structure of Ubc12. Ubc12 has a unique 26-residue N-terminal extension conserved in Ubc12’s across species but not found in other E2s. Following this sequence is the ~150-residue E2 core conserved in all E2s. The position of Ubc12’s catalytic Cys is shown. b, NEDD8 conjugation involves the sequential action of NEDD8’s E1, the heterodimeric APPBP1-UBA3 complex, NEDD8’s E2, Ubc12, a RING E3 Rbx1, and cullin targets2–4,27. c, NEDD8 conjugation to Cul1 was assayed by incubation with purified APPBP1-UBA3 (E1), Ubc12 or Ubc12ΔN lacking residues 2–26 (E2), Rbx1-Cul1 (E3-target complex, lanes 2, 5, 6) or Rbx1-Cul1 Lys720Arg (target complex mutated at NEDD8 modification site, lanes 7–8) as indicated. Lanes 1–4 are controls, lane 5 shows the complete reaction with wild-type Ubc12 and lane 6 shows the reaction with Ubc12ΔN. Lanes 7–8 show that neither Ubc12 nor Ubc12ΔN modify Cul1 with the Lys720Arg mutation. d, Immunoblot control for expression of Ubc12 and Ubc12ΔN in cell proliferation assay. e, Soft agar colony formation assay of NIH 3T3 cells expressing the mutant human CSF-1R[Tyr809Phe] infected with retroviruses empty (top left) or expressing wild type Ubc12 (top right) or the Ubc12ΔN mutant (bottom left) in the presence of human CSF-1. Relative % colony formation is based on controls expressing wild-type human CSF-1R as a reference for 100% (graph, bottom right).
