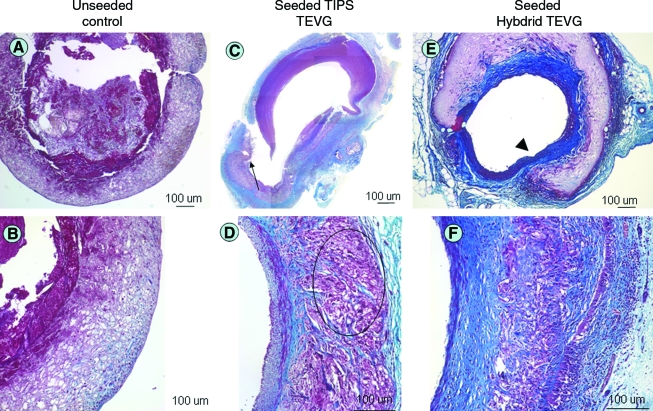
FIG. 4.
Histological findings of TEVG explants. (A) Unseeded controls show intraluminal thrombus with no remodeling of the scaffold. (B) Higher magnification of a different section of the same scaffold as in (A). (C) TIPS TEVG showing newly formed tissue in the inner layer with extensive cell infiltrate and degradation of the scaffold leading to aneurysmal dilation and rupture (arrow). (D) Higher magnification of a different section of the same TIPS scaffold as in (C): giant cells and mononuclear infiltrates are evident within the scaffold (circled area). (E) ES-TIPS scaffold at the anastomosis level showing the transition between native aorta (arrowhead) and the TEVG. (F) Higher magnification at the center of the ES-TIPS TEVG. Color images available online at www.liebertonline.com/ten.