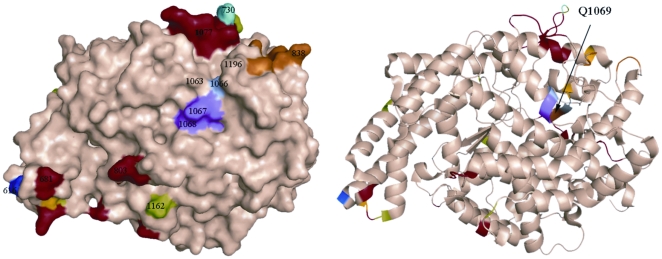
Figure 2. Localization of new mutation (Q1069R) in the C domain of somatic ACE.
The localization of Gln1069 in the C-domain of human ACE which was mutated to Arg is shown using molecular surface (A) and ribbon (B) representations of the substrate-bound crystal structure of the C-domain fragment of human ACE, where the 36 amino acid residues unique to tACE were deleted [75]. The surface and ribbon are light brown, and amino acid residues that were crucial for orientation are colored. Key amino acids referred to in the text are denoted using somatic ACE numbering. Gln1069 (brown) is located right under the bump created by Lys1067 and Tyr1068 (purple) and shown by arrow. Dark blue indicates the first N-terminal amino acid residue (Asp616) seen in this structure; orange-indicates the C terminal end of the C-domain (and the epitope for mAb 1B3; [16], [36]. Light blue (P730) and red colored amino acid residues indicate highly immunogenic bumps on the surface of the C-domain. Light green indicates Asp in putative glycosylation sites.