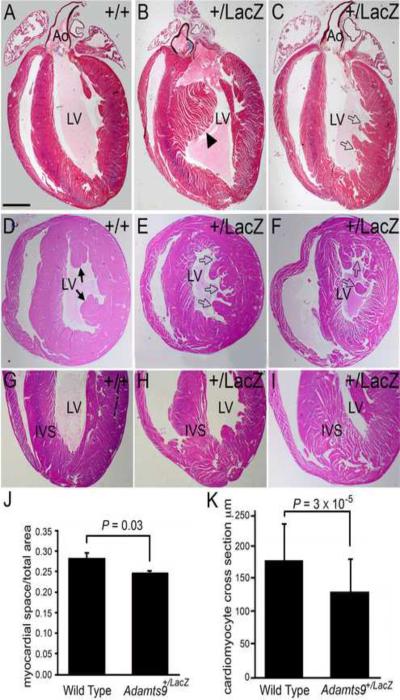
Figure 8. Ventricular myocardium of Adamts9+LacZ heterozygous mice have abnormal myocardial projections.
WT (A,D,G) and Adamts9LacZ heterozygous (B,C,E,F,H,I) adult hearts containing abnormal myocardial projections in the left ventricle (open arrows, solid arrowhead). Frontal sections of adult hearts stained with Movat pentachrome (A–C). Cross sections stained with H&E (D–F). Solid arrowhead in B shows an abnormal interventricular myocardial protrusion. Solid arrows-normal papillary muscles. Adamts9LacZ heterozygous (H, I) frontal adult heart sections stained with H&E showing a wide IVS at the apex and `spongy' appearance. Morphometric analysis of the myocardial space versus the myocardial tissue from WT and Adamts9LacZ heterozygous hearts P = 0.03 (J). A total of 9 Adamts9+/LacZ hearts and 3 WT hearts were analyzed, the approximate lower half of the ventricular myocardium toward the apex as shown in G–I. The resulting P value using Student's t-test 2 tailed, type 2 was P=0.03. Error bars represent one standard deviation of the average presented in the graph (J). Quantification of the individual size of cross sections from WT and Adamts9LacZ heterozygous is also shown; P = 3 × 10−5 (K) using a minimum of 75 Adamts9LacZ and WT cardiomyocytes from 4 different animals. Ao-aorta; LV-left ventricle; IVS-interventricular septum. Magnification bars: A = 475μm applies to B–I.