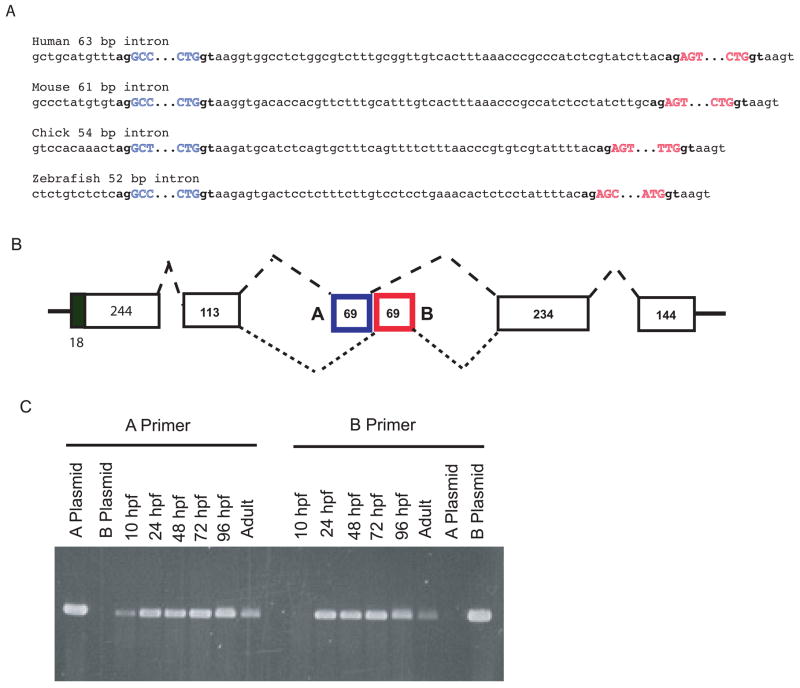
Fig. 8.
(A) Mutually exclusive alternative splicing of exons A and B in pro-α1(V) genes of zebrafish and other species. Sequences are shown of splice junctions and introns separating exons A (blue) and B (red) in the C-propeptide regions of pro-α1(V) genes of human, mouse, chick, and zebrafish. Exonic sequences are uppercase and intronic sequences are lower case. Invariable 5′ gt and 3′ ag ends of introns are in boldface type. (B) A model is shown for the proposed mutually exclusive alternative splicing of exons A and B. (C) RT-PCR with exon A- and B-specific primers demonstrates expression of both exons in col5a1 transcripts of zebrafish embryos and adults. PCR of plasmids containing cloned zebrafish exon A and B sequences (A plasmid and B plasmid, respectively) demonstrates specificity of the primers.