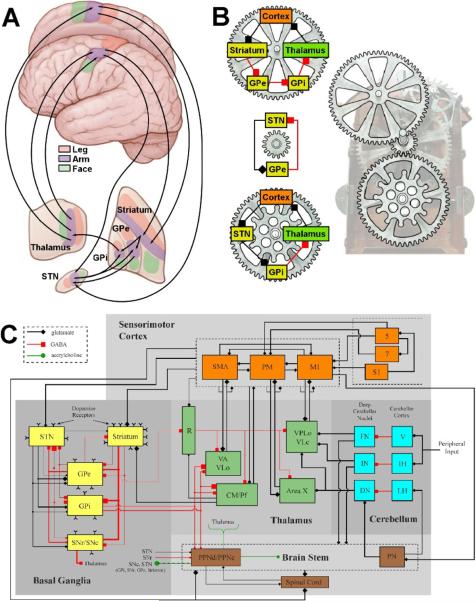
Figure 1.
Network models of the motor circuit. A) Anatomical description of the somatotopically organized cortico-basal-ganglia-thalamo-cortical network. Arrows show some of the sub-circuits within the portion of the motor circuit concerned with the arm. B) Multiple loops exist within the network. Three examples loops are shown, each with a different number of nuclei involved and could be considered oscillators with different periods. Each loop also has at least one nucleus in common with one of the other loops. In turn, these loops interact with each other creating an interlocking system that is part of an even larger system. C) Detailed schematic of the sensorimotor network (adapted from Johnson et al. (2008)). Synaptic terminal shape (square, diamond, circle) signifies the type of neurotransmitter involved, whereas the size of the shape reflects the degree of axonal collateralization in the target nucleus. Within the basal ganglia, line thicknesses represent proportions of each type of projection neuron. Abbreviations are as follows for the cortex (M1: primary motor cortex, PM: premotor cortex, S1: primary somatosensory cortex, SMA: supplementary motor area); the basal ganglia (GPe: globus pallidus pars externa, GPi: globus pallidus pars interna, SNc: substantia nigra pars compacta, SNr: substantia nigra pars reticulata, STN: subthalamic nucleus); the thalamus (CM: centromedian nucleus, Pf: parafascicular nucleus, R: reticular formation of thalamus, VA: ventralis anterior, VLc: ventralis lateralis pars caudalis, VLo: ventralis lateralis pars oralis, VPLo: ventralis posterolateralis pars oralis); the cerebellum (DN: dentate nucleus, FN: fastigial nuclei, IH: intermediate hemisphere of cerebellum, IN: interposed nuclei, LH: lateral hemisphere of cerebellum, V: vermis); and the brain stem (PN: pontine nucleus, PPNc: caudal pedunculpontine nucleus, PPNd: dorsal pedunculopontine nucleus).