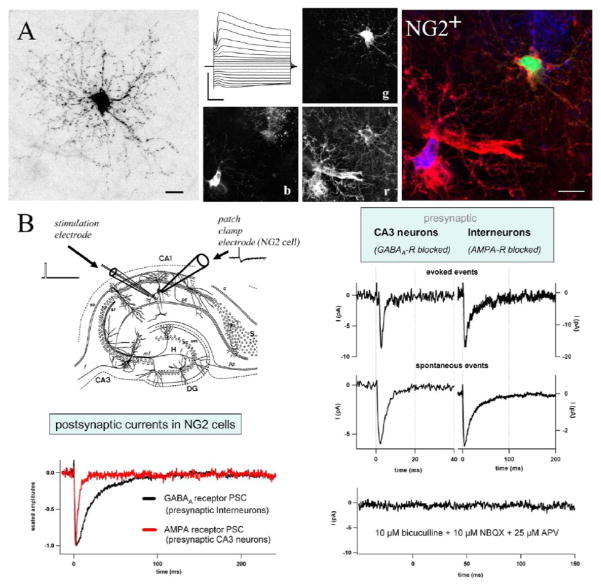
Figure 1.
Properties of synaptic inputs to NG2 cells in an acute slices of hippocampus from juvenile transgenic hGFAP/EGFP mice. (A) The morphology of NG2 cells was visualized by Texas Red dextran-filling during whole-cell recording. Subsequent confocal analysis and 2D maximum projection shows the extensive arborization of their processes. Note the typical nodules appearing as dots all along the fine processes (bar 10 μm). A typical current pattern is given in the middle panel. Current responses were evoked by de- and hyperpolarizing the membrane between +20 and −160 mV (holding potential −80mV, 10 mV steps, bars 1 nA, 10 ms). Post-recording immunostaining and triple fluorescence confocal analysis were applied to test for NG2 immunoreactivity. The middle panel shows three separated colour channels of one confocal plane. Texas Red dextran labelling is given in green (g), NG2 immunoreactivity in red (r), and EGFP expression in blue (b). The superimposed RGB picture (right) shows the membrane-associated distribution of NG2 immunoreactivity of the recorded cell (yellow details). (B) Postsynaptic currents were recorded from an NG2 cell upon short single pulse stimulation. At least two types of presynaptic neurons, glutamatergic CA3 pyramidal neurons and GABAergic interneurons, innervate hippocampal NG2 cells. Corresponding glial postsynaptic currents can be distinguished by their current kinetics and their pharmacological profiles. Modified from Jabs et al. (2005).