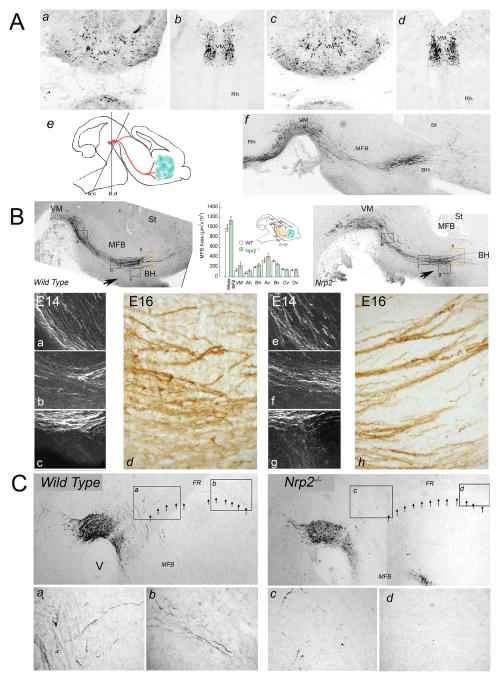
Figure 8. The meso-telencephalic DA pathway appears unaffected in Nrp2-/- mice.
(A) 20 μm coronal sections from wild type (a,b) and Nrp2-/- mouse E16 embryos (c,d) were cut at different angles (e) to better visualize the aberrant growth of DA neurites. Most Nrp2-/- brains showed a normal TH+ fiber and cell organization in the VM. Only one Nrp2-/- mouse out of 16 (f) showed TH+ cells and axons extending caudally into the rhombencephalon (compare with B). (B) Twenty micron parasagittal tissue sections were cut from E12-16 wild type and Nrp2-/- mouse embryos as depicted in Fig. 1 and stained for TH. The number and organization of the Nrp2-/- VM DA neurons were undistinguishable from wild type. TH+ fibers running along the MFB have similar ventro-dorsal organization in E16 wild type and Nrp2-/- mouse brains. The area occupied by the MFB was measured in 3 to 5 parasagittal sections from 3 wild type and mutant mice. The graph shows the area of the whole MFB measured from the rostral end of the mesencephalic flexure to the internal capsule. The area occupied by the MFB was also measured in 500 μm wide segments distributed in 3 rows (VM, Ah, Bh) and 4 columns (Av-Dv) along the track. Although the MFB of Nrp2-/- embryos seems to spread dorsally no significant differences were found with the wild type. High magnification of the areas framed in the upper panels show detail of TH+ axons running along the MFB in E14 (a,b,c) and E16 (d,e) brains. Note that the degree of fasciculation of the TH+ axons is similar in both wild type and Nrp2-/- brains. Arrows indicate TH+ axons entering the basal hypothalamus (BH). (C) The DA mesohabenular pathway running along the fasciculus retroflexus (FR, arrows) was severely disturbed by the Nrp2-/- mutation. (ad): High magnification of the areas framed in the upper panels showing TH+ fibers running along the FR. Note the virtual disappearance of these fibers in the Nrp2-/- mouse.