FIG. 3.
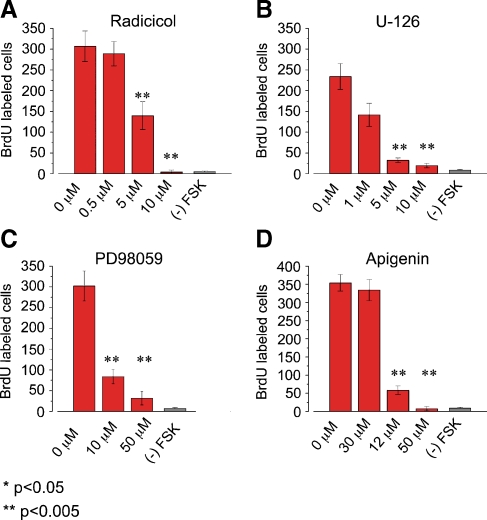
Multiple ERK MAPK inhibitors block FSK-induced BrdU incorporation. Cochlear explants were cultured for 72 h with 100 µM FSK in standard medium in the presence or absence of the indicated ERK MAPK inhibitors at various concentrations. After 72 h in culture cochleas were fixed and processed for immunocytochemistry. The standard media contained 10% fetal calf serum and 0.01% BrdU. A Bar graph showing the average number of FSK-induced BrdU-labeled nuclei per cochlea in the presence of various concentrations of the Raf inhibitor Radicicol. The presence of 5 and10 µM Radicicol significantly inhibited FSK-induced BrdU incorporation compared with presence of 0.5 µM Radicicol and 0 µM Radicicol (p < 0.005; Radicicol IC50 −1 µM). The average number of BrdU labeled cells per cochlea was 307 ± 36.9 for 0 µM Radicicol; n = 7, 289 ± 29.2 for 0.5 µM Radicicol, n = 9; 140 ± 33.5 for 5 µM Radicicol, n = 7; 4.1 ± 4.9 for 10 µM Radicicol, n = 8; and 3.9 ± 4.9 for (–) FSK, n = 5. B Bar graph showing the average number of FSK-induced BrdU-labeled nuclei per cochlea in the presence of various concentrations of the MEK-1/2 inhibitor U-126. The presence of 5 and10 µM U-126 significantly inhibited FSK-induced BrdU incorporation compared with presence of 1 µM U-126 and 0 µM U-126 (p < 0.005; U-126 IC50 −1 µM). The average number of BrdU labeled cells per cochlea was 234 ± 30.7 in the presence of 0 µM U-126, n = 4; 142 ± 28.2 in the presence of 1 µM U-126, n = 5; 32.4 ± 5.3 in the presence of 5 µM U-126, n = 5; 19.6 ± 5.5 in presence of 10 µM U-126, n = 8; and 5.8 ± 1.9 for (–) FSK, n = 4. C Bar graph showing the average number of FSK-induced BrdU-labeled nuclei per cochlea in the presence of various concentrations of the MEK-1/2 inhibitor PD98059. The presence of 10 and 50 µM PD98059 significantly inhibited FSK-induced BrdU incorporation compared with the presence of 0 µM PD98059 (p < 0.005; PD98059 IC50 −10 µM). The average number of BrdU labeled cells per cochlea was 302 ± 35.8 in the presence of 0 µM PD98059, n = 6; 83.8 ± 17.4 in the presence of 10 µM PD98059 n = 6; 31.7 ± 15.9 in the presence of 50 µM PD98059, n = 6; and 5.5 ± 2.9 for (–) FSK, n = 5. D Bar graph showing the average number of FSK-induced BrdU-labeled cells per cochlea in the presence of various concentrations of the ERK-1/2 inhibitor Apigenin. The presence of 30 and 50 µM Apigenin significantly inhibited FSK-induced BrdU incorporation compared with the presence of 12 µM Apigenin and 0 µM Apigenin (p < 0.005; Apigenin IC50 −25 µM). The average number of BrdU labeled cells per cochlea was 354 ± 22.9 in the presence of 0 µM Apigenin, n = 4; 334 ± 42.6 in the presence of 12.5 µM Apigenin, n = 4; 58.3 ± 12.1 in the presence of 30 µM Apigenin, n = 4; 7 ± 6 in presence of 50 µM Apigenin, n = 4; 10 ± 5.4 in presence of 75 µM Apigenin, n = 4; and 5.5 ± 2.9 for (–) FSK, n = 4.