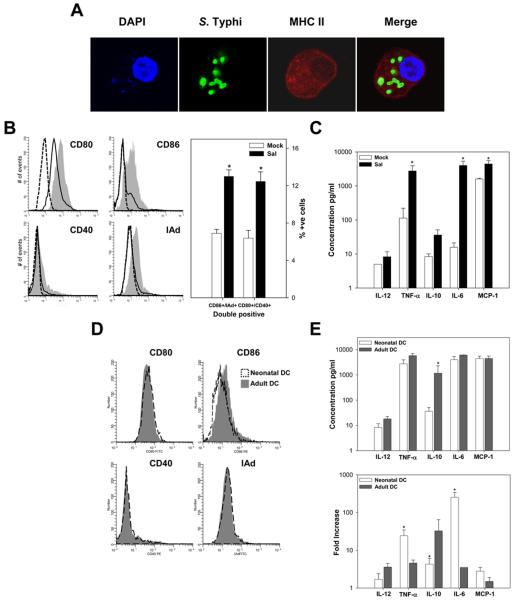
FIGURE 6.
S. Typhi induces activation and maturation of neonatal DC. A, Confocal laser microscopy images of CD11c+ DC treated with S. Typhi for 2 h. FITC anti-common Salmonella Ag-1 mAb was used to detect S. Typhi; DC were stained with a purified MHC class II (I-Ad) mAb followed by Alexa Fluor 546 anti-mouse IgG; 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride was used to show the nuclei. Images shown are representative from the mid-plane of the cell. B, Expression of costimulatory molecules (CD80, CD86, CD40, and MHC class II (I-Ad)) on CD11c+ BM-derived neonatal DC after S. Typhi (gray-filled histogram) or mock-infection (solid line); dashed line indicates isotype control staining. Right panel, Shows percent of CD11c+ simultaneously expressing CD86/I-Ad and CD80/CD40 ± SEM; results are mean from three independent experiments. C, Cytokines produced by neonatal BM-derived DC upon S. Typhi or mock-infection measured in culture supernatants. Data represent mean cytokine concentration ± SEM from three independent experiments. Significant differences (*, p <0.05) compared with the mock-infected cells. D and E, Comparison on surface markers levels (D) and cytokine levels and fold increase (E) between S. Typhi treated neonatal and adult DC. Significant differences (*, p <0.05) compared with the adult-infected cells. Both adult and newborn CD11c+ stimulated with LPS (control) showed increased expression of activation and maturation markers and enhanced cytokine production (data not shown).