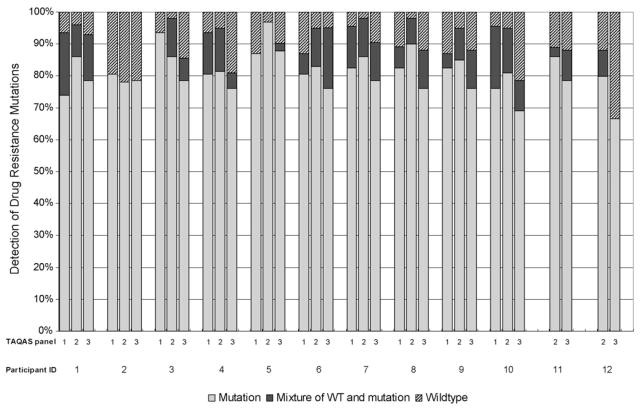
Fig. 2.
The participants’ detection of drug resistance mutations (DRMs) at nucleotide sequences positions associated with ARV drug resistance in the target genotype (TG). Most participants reported >80% of the DRMs present in the TG as mutations (grey bars) or nucleotide mixtures of wildtype and mutation (black bars). Participants’ sequences varied in the percent of DRMs reported as nucleotide mixtures (black bars). Some participants reported wildtype at >20% of the nucleotide sequences positions associated with ARV drug resistance in the TG (hatched bars).