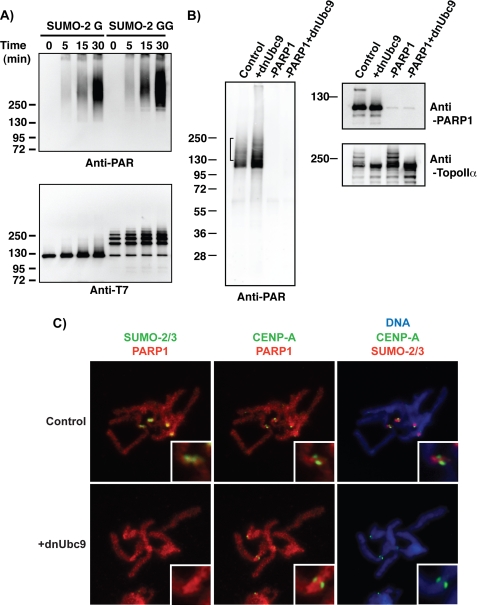
FIGURE 5.
Inhibition of SUMOylation on mitotic chromosomes alters chromosomal PARylation. A, SUMOylated PARP1 retains robust enzymatic activity of poly-ADP-ribosylation in vitro. An in vitro SUMOylation reaction was performed in the presence of the indicated SUMO-2 proteins as in Fig. 3. After the SUMOylation reaction, NAD+ was added to the reaction mixture, and then the reaction mixture was incubated for the indicated periods. Poly(ADP-ribosyl) chain formation was analyzed by a monoclonal anti-PAR antibody (Trevigen). PARP1 was detected with an anti-T7 antibody. B, SUMOylation affects PARylation on chromosomes prepared from XEE. Mitotic chromosomes were isolated from the extracts that were manipulated as indicated. Isolated chromosomal fractions were incubated with NAD+-containing buffer to promote PARylation on chromosomal proteins, and then the reactions were terminated with the addition of SDS-PAGE sample buffer. The obtained chromosomal samples were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. The bracket indicates the area of PARylation signals affected by the inhibition of SUMOylation. C, inhibition of SUMOylation does not affect localization of PARP1 on mitotic chromosomes significantly. CSF extracts were released into interphase by CaCl2 addition. 200 sperm/μl were added 5 min after CaCl2, and the extract was incubated at 23 °C for 55 min. Reentry into mitosis was induced by the addition of fresh CSF extract (50% of reaction volume) with or without dnUbc9 (150 ng/μl final concentration). Chromosomes from each reaction were spun onto coverslips and analyzed by immunofluorescence with antibodies against SUMO-2/3, PARP1, and CENP-A as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Each signal was pseudocolored as indicated at the top of the panels. DNA was visualized with Hoechst 33342 staining. Insets are magnified images around the centromere region.