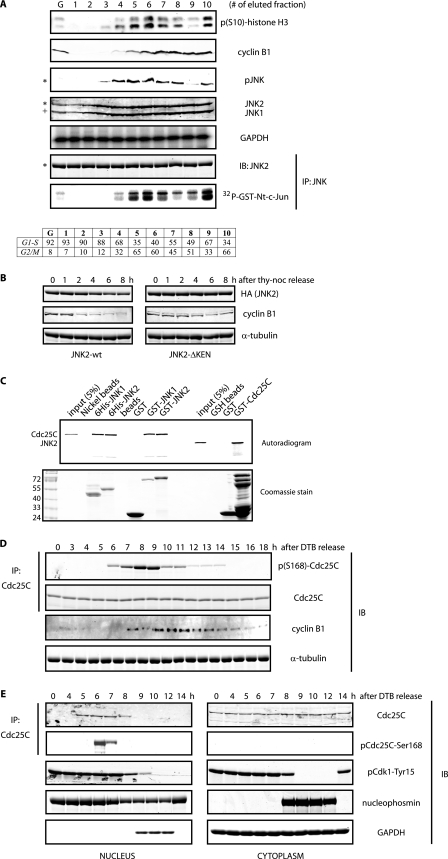
FIGURE 1.
Cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of Cdc25C by JNK. A, HeLa cells were fractionated by elutriation, and extracts prepared from elutriated cells were analyzed either by immunoblotting (IB) with the indicated antibodies or by immunokinase assays for JNK. G refers to exponentially growing cells, and fractions 1–4 correspond to cells in interphase, whereas fractions 5–10 correspond to cells in mitotic stages, as indicated by the FACS analysis (bottom table). The asterisk refers to the 54-kDa JNK2 isoform, and + refers to the 46-kDa JNK1 isoform present in HeLa cells. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; IP, immunoprecipitation. B, HeLa cells were transfected with hemagglutinin (HA)-tagged either JNK2 wild type or KEN-deleted mutant and arrested in prometaphase by means of a thymidine-nocodazole (noc) protocol and then released for the indicated time points. Levels of hemagglutinin-tagged JNK2 and cyclin B1 were monitored by immunoblotting. Tubulin was used as a loading control. C, in vitro binding assay between JNKs and Cdc25C using bacterially purified recombinant proteins and reticulocyte extracts programmed to produce radiolabeled proteins as indicated. D, HeLa cells were synchronized along the cell cycle by a double-thymidine block (DTB) in G1/S and then released and analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies during a 18 h kinetic. E, shown is a similar analysis as in D, but cells were fractionated into nuclear and cytosolic extracts. B and E, images originate from the same gel/membrane.