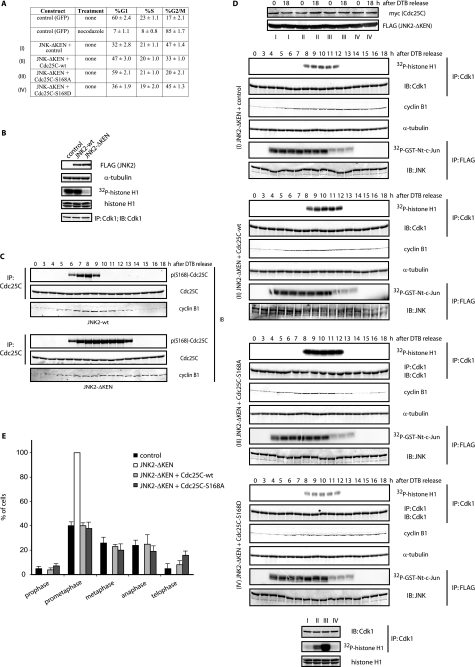
FIGURE 2.
JNK-mediated Cdc25C phosphorylation regulates cell cycle. A, FACS analysis of HFF-1 cells expressing the indicated plasmids for 48 h is shown. The percentage (%) of cells in G1, S, and G2/M is indicated as the mean ± S.D. for three independent experiments. B, HeLa cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged either JNK2-wild type (wt) or KEN-deleted mutant for 24 h. Cell extracts from mitotic cells (obtained by mitotic shake-off) were prepared and analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) using the indicated antibodies and Cdk1 immunokinase assays. IP, immunoprecipitation. C, HeLa cells were transfected with either JNK2 wild type (wt) or KEN-deleted mutant, synchronized by a double-thymidine block (DTB), and released into the cell cycle and analyzed by immunoblotting for cyclin B1, Cdc25C, and phosphorylated Cdc25C at serine 168 levels. D, HFF-1 cells were cell cycle-synchronized by a double-thymidine block and nucleofected with empty plasmid (control), the JNK2-ΔKEN mutant alone or together with wild-type Cdc25C, non-phosphorylatable mutant (S168A), or phosphomimetic mutant (S168D) of Cdc25C, as indicated (conditions I–IV), and analyzed by immunoblotting or immunokinase assays for either Cdk1 (using histone H1 as substrate) or JNK (using a glutathione S-transferase (GST)-tagged N terminal fragment of c-Jun (amino acids 1–89) as substrate). The bottom panels show Cdk1 activity in the four different conditions (I–IV) as assessed in a same gel for comparison. E, HFF-1 cells were nucleofected with the indicated plasmids for 48 h, fixed, and stained for tubulin and DNA, and the percentage of cells in the different mitotic stages was quantified as indicated under “Experimental Procedures.”