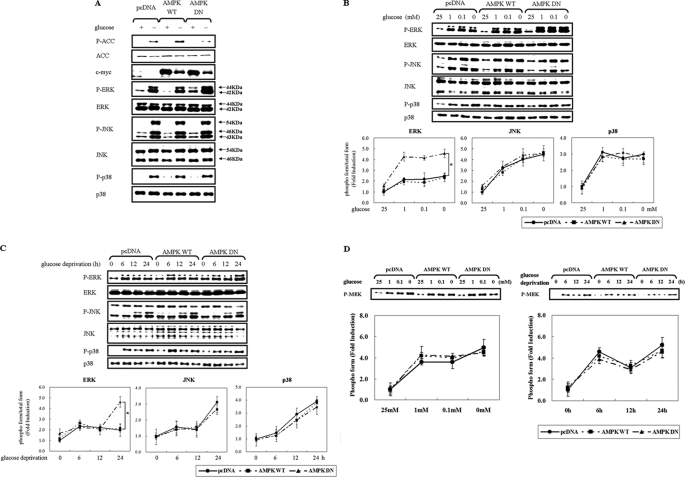
FIGURE 1.
Inhibition of AMPK potentiates glucose deprivation-induced ERK activation in a MEK-independent manner. HCT116p53+/+ cells were transfected with pcDNA or c-myc-tagged pAMPK-WT or pAMPK-DN expression vector for 24 h and exposed to glucose deprivation for 24 h (A), the indicated concentration of glucose for 24 h (B, D), or glucose-free medium for the indicated time period (C, D). Under these conditions, the phosphorylated form of the indicated protein (P-ACC, P-ERK, P-JNK, P-p38, P-MEK) and the total form (ACC, ERK, JNK, p38, c-myc) was examined via Western blot analyses using specific antibodies. Experiments were repeated four times with similar results, and a representative result is shown. Each band was analyzed and quantified by densitometer. The data are expressed as the means ± S.E. (*, p < 0.05; compared with the indicated groups).