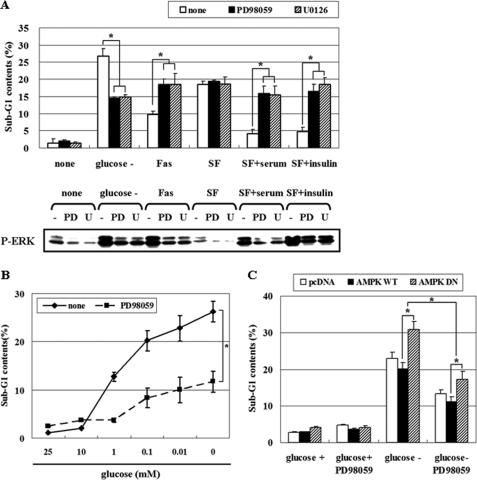
FIGURE 9.
ERK has contrasting effects depending on the stimulus, and AMPK protects cells from glucose deprivation-induced apoptosis via suppressing pro-apoptotic ERK. A, HCT116p53+/+ cells were pretreated with two different MEK inhibitors, PD98059 (25 μm) or U0126 (10 μm), for 30 min, and then cells were exposed for 24 h to glucose-deprived medium, Fas (CD95/Apo-1)-activating mouse anti-Fas monoclonal antibody (Fas), 10% serum, or insulin (100 nm) following 12 h of serum starvation. Cells were then subjected to fluorescence-activated cell scanning analysis for the percentage of nuclei containing subdiploid amounts of DNA (sub-G1 fraction) (upper panel) and phosphoactivated ERK (P-ERK) was measured (lower panel). B, HCT116p53+/+ cells were exposed to a medium containing the indicated concentrations of glucose for 24 h with or without 25 μm PD98059 and then analyzed for apoptosis via fluorescence-activated cell scanning analysis. C, HCT116p53+/+ cells were transfected with pcDNA, pAMPK-WT, or pAMPK-DN expression vectors for 24 h and maintained under glucose deprivation for 24 h with or without PD98059 (25 μm). The sub-G1 fraction of the cells was measured as a percentage. Experiments were repeated three times with similar results, and a representative result is shown. (*, p < 0.05; compared with the indicated groups.)