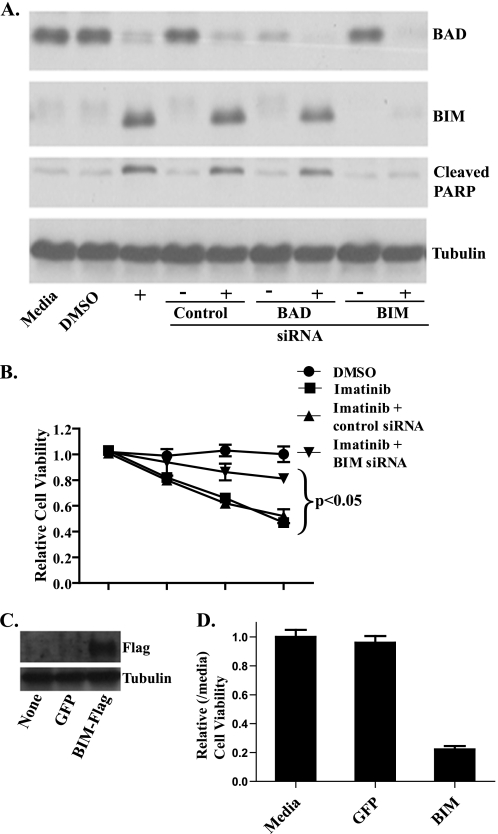
FIGURE 2.
BIM knockdown by siRNA protects GIST 882 cells from imatinib-induced cell death, and, conversely, BIM overexpression induces cell death. A, GIST 882 cells were treated with control siRNA or siRNA targeting BIM or Bad, followed by treatment with 1 μm imatinib for 48 h prior to whole-cell lysis and Western blot analysis. Blots were probed with antibodies specific to Bad, BIM, tubulin (loading control), and cleaved poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, a marker for apoptosis. B, GIST 882 cells were treated with siRNA and 1 μm imatinib as in A, and then cell viability was assayed using the CellTiter-Glo ATP luminescence assay after 24, 48, or 72 h. The data were normalized to untreated medium controls and represent mean values (±S.D.) of three experiments. p < 0.05 indicates a significant difference between BIM siRNA and imatinib compared with control siRNA and imatinib or imatinib without siRNA. C, Western blot analysis of whole-cell lysates prepared from GIST 882 cells 24 h following transfection with a BIM-FLAG or green fluorescent protein (GFP) control vector. Blots were probed with antibodies specific to FLAG and tubulin. D, GIST 882 cells were transfected with either BIM-FLAG or green fluorescent protein, and then cell viability was assayed using the CellTiter-Glo ATP luminescence assay after 36 h. The data were normalized to untreated, medium controls.