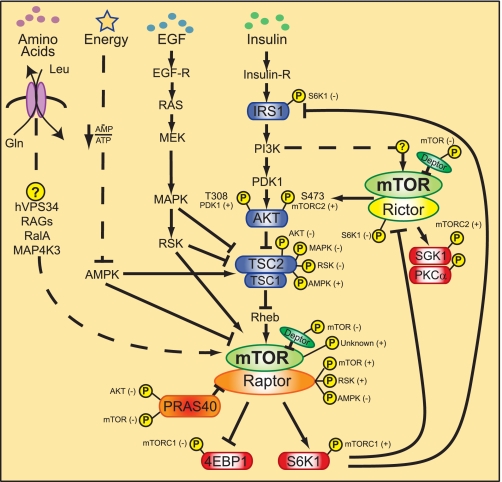
FIGURE 2.
Regulation of mTORC signaling networks. Growth factors/mitogens (insulin, EGF) and nutrients (e.g. amino acids, energy) promote mTORC1 signaling via phosphorylation cascades that converge on TSC and the mTORCs themselves. Insulin signals via its receptor (Insulin-R) to activate the PI3K/Akt/TSC/Rheb pathway; EGF signals via its receptor (EGF-R) to activate the Ras/MEK/MAPK/RSK pathway; amino acid sufficiency signals via hVps34 and the RAG and RalA GTPases; and energy sufficiency suppresses AMPK. Insulin/PI3K signaling likely promotes mTORC2 signaling via an unknown pathway. An mTORC1/S6K1-mediated negative feedback loop signals via two pathways to suppress PI3K/mTORC2/Akt signaling. Arrows versus blocked lines indicate activation or inhibition of protein function, respectively, by an upstream regulator. Phosphorylation events (denoted by circled yellow P) known to modulate protein function are shown. The kinases responsible for phosphorylation events are also indicated, with (+) or (−) denoting activation or inhibition of protein function, respectively.