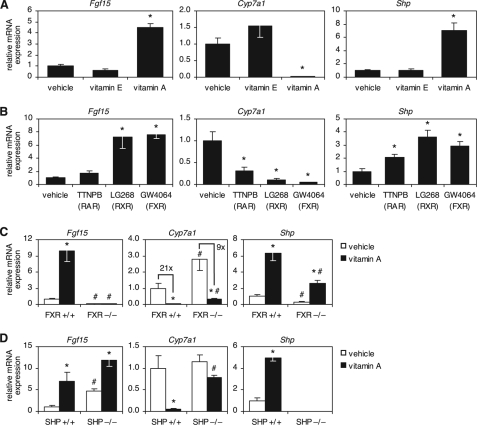
FIGURE 3.
Vitamin A induces Fgf15 and Shp to suppress Cyp7a1. A, wild-type mice were treated for 16 h by oral gavage with 500 mg/kg d-α-tocopherol (vitamin E) or 100 mg/kg retinyl palmitate (vitamin A). mRNA expression in the ileum (Fgf15) and liver (Cyp7a1 and Shp) was determined by quantitative RT-PCR, normalized to U36b4, and graphed relative to the vehicle-treated control. B, wild-type mice were treated for 1 day with diets containing the indicated synthetic ligands. The target nuclear receptor is shown in parentheses. Data analysis was as described for A. C and D, mice of the indicated genotype were treated for 16 h by oral gavage with 100 mg/kg retinyl palmitate (vitamin A). mRNA expression in the ileum (Fgf15) and liver (Cyp7a1 and Shp) was determined by quantitative RT-PCR, normalized to U36b4, and plotted relative to the wild-type vehicle-treated control. For all panels, data represent the mean ± S.E. of five animals/group. *, p < 0.05 compared with the vehicle of the same genotype; #, p < 0.05 compared with the wild type of the same treatment group.