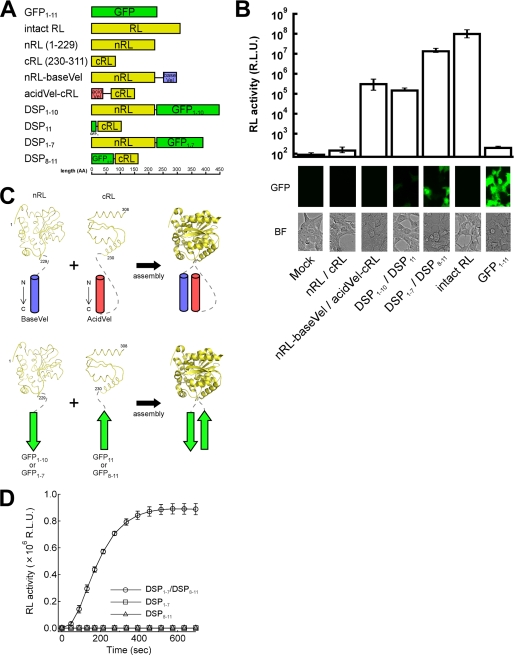
FIGURE 1.
Design and complementation efficiency of split proteins. A, shown are the constructs used in this study. GFP1–11 and intact RL, a full-length green fluorescent protein and Renilla luciferase; nRL and cRL, the N- or C-terminal fragment of spRL (13); baseVel and acidVel, a derivative of the heterodimeric leucine zipper containing basic or acidic residues (16); DSP, dual split protein composed of fragments of spGFP and spRL. The β-sheet contained within each spGFP is indicated by subscripts. The bottom bar indicates a scale in amino acids (AA). B, shown is the result of the complementation. The activities of RL (upper panel) and GFP (lower panel) were determined after 36 h of co-transfection in 293FT cells. R.L.U., relative light units. The bright field (BF) images are also shown. All the abbreviations are same as A. C, the schematic diagram of the arrangement of the association modules and target spRL is shown. The shown structures of spRL were generated based on the reported structure of RL (22). The number at the terminus of each chain indicates the position of the residue. The gray dashed line indicates the linker region. Top panel, the pattern of assembly of spRL with AcidVel (red) and BaseVel (blue) motives is shown. Bottom panel, the pattern of association of spRL with the self-assembling spGFPs (green) is shown. The spGFP-1 and -2 indicates the N-terminal fragment and C-terminal fragment of spGFP, respectively. D, shown are the kinetics of the complementation of DSP in a cell-free system. The cell lysates containing DSP1–7 or DSP8–11 prepared from the transfected 293FT cells were mixed (DSP1–7/DSP8–11), and the recovered RL activity was monitored in a time-dependent manner. Individual DSP alone (DSP1–7 or DSP8–11) showed no activities. The data are averages of three or more independent experiments.