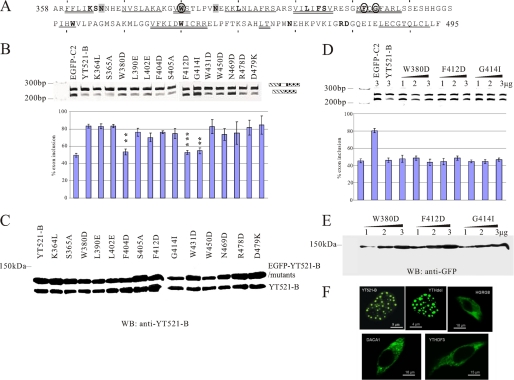
FIGURE 6.
Mutational analysis of the YTH domain. A, sequence of the YTH domain found in YT521-B (6). The region corresponds to amino acids 358–495. Starting from amino acid 360, every 10th amino acid is indicated with a dash. The phylogenetically conserved residues are indicated by bold letters. The regions predicted to form α helices or β strands are indicated. α-helix: double line, β-sheet: single line. Residues important for influencing splice site selection are circled. Residues that contact RNA are shaded. B, analysis of the MG-YT2 minigene in cotransfection experiments with YTH domain mutations that are indicated by the amino acids changed. p values are 0.0092 (W380D), 0.0038 (F412D), and 0.007 (G414I). C, expression analysis of YTH domain mutations by Western blot, using an antiserum against YT521-B (7). D, analysis of three YTH-domain mutations most severely affecting the YTH domain. 1–3 μg of expression plasmids for each construct were transfected with the MG-YT2 reporter minigene and analyzed by RT-PCR. Parental vector is always included to give comparable amounts of transfected plasmid. The images underneath show the statistical evaluation of three independent experiments and the increase of expression of each mutant, which was detected by Western blot of cellular lysates using an antibody against EGFP. E, localization of YTH-domain containing proteins. Proteins that were tagged with EGFP at the N terminus were expressed in HEK293 cells. The images show representative cells. YT521-B and YTHdel are localized in the nucleus. The images are enlarged to show the nuclear substructure.