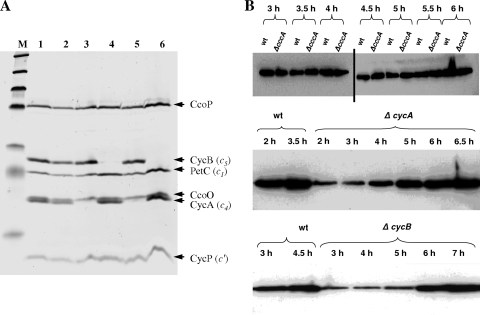
FIG. 1.
(A) SDS-PAGE gel of the cccA, cycA, and cycB mutants stained for covalently bound heme. N. gonorrhoeae strains F62 (lane 1), JCGC851 (cccA) (lane 2), JCGC800 (cycA) (lane 3), JCGC850 (cycB) (lane 4), JCGC853 (cccA cycA) (lane 5), and JCGC852 (cccA cycB) (lane 6) were grown on plates at 37°C in a candle jar overnight. Samples were collected, lysed, and separated by SDS-PAGE. The gel was then heme stained to detect c-type cytochromes. (B) Western analysis of the accumulation of AniA as cultures became oxygen limited. Equivalent amounts of bacterial biomass were loaded onto each track of all the gels shown. (Top) Comparison of the cccA mutant that lacks the cytochrome c2 gene with parental strain F62. Tracks on either side of the vertical black bar were from independent gels. (Middle) Comparison of strain F62 with the cycA mutant that lacks cytochrome c4. (Bottom) Comparison of F62 with the cycB mutant that lacks cytochrome c5.