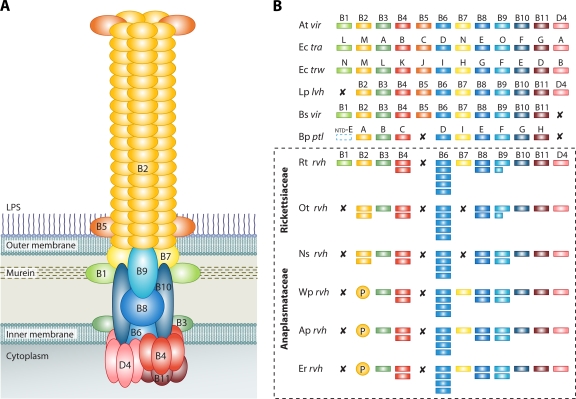
FIG. 1.
P-T4SSs. (A) Model of the vir P-T4SS encoded on the pTi plasmid of A. tumefaciens. B1 to B11, VirB1 to VirB11; D4, VirD4. (B) Comparison of the rvh P-T4SSs from Rickettsiales with similar P-T4SSs from other bacteria. At vir, A. tumefaciens Ti plasmid P-T4SS; Ec tra, E. coli IncN plasmid pKM101 P-T4SS; Ec trw, E. coli plasmid R388 P-T4SS; Lp lvh, L. pneumophila P-T4SS; Bs vir, Brucella suis P-T4SS; and Bp ptl, B. pertussis P-T4SS. VirB1 of B. pertussis is depicted with the N-terminal glycohydrolase domain of PtlE (ntd-E) (107). The rvh examples are shown within the dashed-line box: Rt rvh, R. typhi P-T4SS; Ot rvh, O. tsutsugamushi P-T4SS; Ns rvh, Neorickettsia sennetsu P-T4SS; Wp rvh, Wolbachia pipientis P-T4SS; Ap rvh, A. phagocytophilum P-T4SS; and Er rvh, Ehrlichia ruminantium P-T4SS. X indicates that no gene for the component has been annotated and no subjects were detectable using tblastn; P represents the proliferation of rvhB2 genes, putative VirB2-like encoding genes.