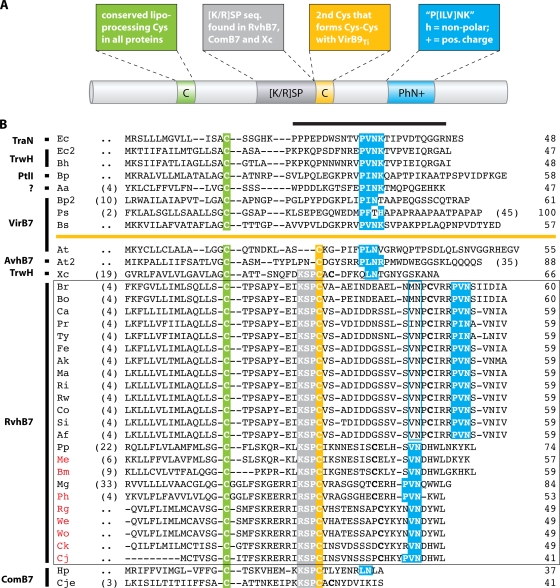
FIG. 4.
P-T4SS lipoproteins. (A) Schematic depiction of typical characteristics of VirB7 and related proteins. The color scheme is used to identify distinct features in the alignment (see the text for explanation). (B) Manual alignment of 13 diverse VirB7 and VirB7-like lipoproteins with 23 RvhB7 lipoproteins (the latter are boxed). Coordinates for each sequence are shown to the right, with numbers in parentheses to the left referring to flanking residues not shown in the alignment. Protein annotation is shown to the left. The black horizontal bar over the sequences of the predicted processed lipoproteins identifies the region of the NMR structure for the interaction of the TraO C-terminal domain (VirB9-like protein) and TraN (VirB7), both encoded by plasmid pKM101 in E. coli. Sequences above the orange line depict lipoproteins without a predicted Cys-Cys interaction with VirB9 and VirB9-like proteins: Ec, E. coli TraN, encoded by plasmid pKM101 (accession no. NP_511194); Ec2, E. coli TrwH protein (accession no. FAA00034); Bh, B. henselae TrwH-like protein (accession no. AAM82208); Bp, B. pertussis TraI protein, encoded by plasmid pSB102 (accession no. NP_361043); Aa, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans lipoprotein (accession no. NP_067577); Bp2, B. pertussis putative bacterial secretion system protein (accession no. NP_882291); Ps, P. syringae subsp. syringae VirB7 (accession no. NP_940729); and Bs, B. suis VirB7 (accession no. AAN33275). Sequences below the orange line represent proteins predicted to interact with VirB9 and VirB9-like proteins via a Cys-Cys bond: At, A. tumefaciens VirB7 (accession no. NP_536291); At2, A. tumefaciens AvhB7 (accession no. NP_396098); Xc, X. citri VirB7 (accession no. NP_942612); Br, R. bellii strain RML 369-C RvhB7 (accession no. YP_538183); Bo, R. bellii strain OSU 85 389 RvhB7 (accession no. YP_001495873); Ca, R. canadensis strain McKiel RvhB7 (accession no. YP_001492545); Pr, R. prowazekii strain Madrid E RvhB7 (accession no. NP_220672); Ty, R. typhi strain Wilmington RvhB7 (accession no. YP_067241); Fe, R. felis strain URRWXCal2 RvhB7 (accession no. YP_246480); Ak, R. akari strain Hartford RvhB7 (accession no. YP_001493229); Ma, R. massiliae strain MTU5 RvhB7 (accession no. YP_001499186); Ri, R. rickettsii strain Sheila Smith RvhB7 (accession no. YP_001494506); Rw, R. rickettsii strain Iowa RvhB7 (accession no. YP_001649753); Co, R. conorii strain Malish 7 RvhB7 (accession no. NP_360023); Si, R. sibirica strain 246 RvhB7 (accession no. ZP_00142155); Af, R. africae strain ESF-5 RvhB7 (accession no. ZP_02336216); Pp, protein of the Wolbachia symbiont of C. quinquefasciatus (accession no. YP_001975581); Me, protein of the Wolbachia symbiont of D. melanogaster; Bm, protein of the Wolbachia symbiont of Brugia malayi; Mg, A. marginale protein (accession no. YP_153652); Ph, A. phagocytophilum protein; Rg, E. ruminantium strain Gardel protein; We, E. ruminantium strain Welgevonden (Erwe) protein; Wo, E. ruminantium strain Welgevonden (Erum) protein; Ck, E. chaffeensis strain Arkansas protein; Cj, E. canis strain Jake protein; Hp, H. pylori protein (accession no. CAA10654); and Cje, C. jejuni protein (accession no. NP_863349). RvhB7 taxon codes colored red indicate that sequences corresponding to putative unannotated ORFs were recovered from tblastn searches of the Anaplasmataceae database (sequence coordinates are listed in Table S2 in the supplemental material). Additional conserved Cys residues in the RvhB7 sequences are in bold. A second putative PhN+ motif in the Rickettsia RvhB7 sequences is shaded in blue.