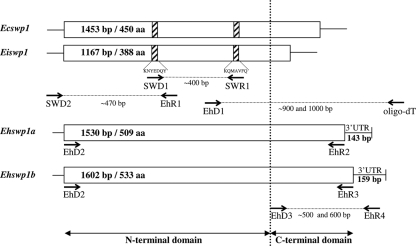
FIG. 2.
PCR strategy used for the amplification of the genes encoding EhSWP1a and EhSWP1b. The first-round PCR was performed using degenerated primers SWD1 and SWR1 designed from conserved amino acid regions (hatched parts) in SWP1s of E. cuniculi (EcSWP1) and E. intestinalis (EiSWP1). The 5′-end region of swp1 genes was completed using SWD2 and EhR1. The 3′-end regions, including the 3′-untranslated regions (UTR), were then determined by RT-PCR with an oligo(dT) primer. After reverse transcription, the PCRs were performed using the primer corresponding to the adapter sequence linked to oligo(dT) and the forward primer EhD1 designed from the previously amplified 400-bp DNA sequence. The full open reading frames (ORFs) were finally validated through amplification with EhD2 and either EhR2 for Ehswp1a or EhR3 for Ehswp1b. The primer pair EhD3-EhR4 was used to analyze the polymorphism of the C-terminal part of SWP1s in four E. hellem isolates. EhD3 was designed from a conserved amino acid region between EhSWP1a and EhSWP1b (TTASGD) located upstream of their divergent C terminus. EhR4 was designed in a conserved part of the 3′-UTR of both EhSWP1a and EhSWP1b.