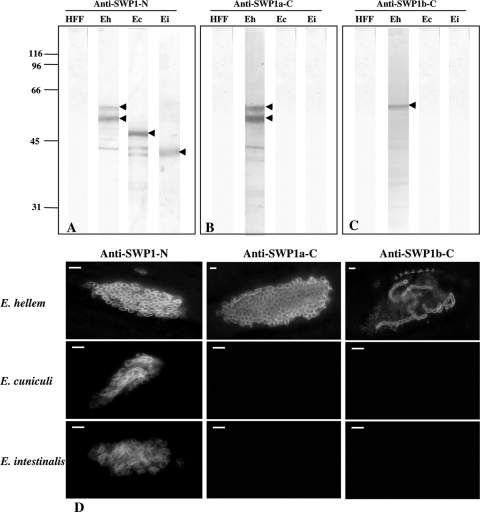
FIG. 4.
Immunodetection of SWP1-like proteins by Western blotting and IFA. (A to C) Western blot analyses were performed after SDS-PAGE on protein extracts from healthy human fibroblast cells (HFF) and HFF cells infected by E. cuniculi (Ec), E. intestinalis (Ei), and E. hellem (Eh) using antisera against SWP1-N (A), SWP1a-C (B), and SWP1b-C (C). Two major bands at 55 and 60 kDa (arrowheads) are detected for E. hellem with anti-SWP1-N (A) and anti-SWP1a-C (B), whereas sera raised against SWP1b-C only recognize the 60-kDa band (C; arrowhead). When using the anti-SWP1-N antibodies, cross-hybridizations are observed with an ∼50-kDa band for E. cuniculi and an ∼40-kDa band for E. intestinalis (A; arrowheads). (D) Indirect-immunofluorescence assay (IFA) with the three anti-SWP1 antisera. Antisera were applied to HFF cells 96 h postinfestation with E. hellem, E. cuniculi, or E. intestinalis. Cell surface labeling of most E. hellem intracellular stages is observed with anti-SWP1-N and anti-SWP1a-C, whereas only a few intracellular parasites are stained with anti-SWP1b-C. Antibodies specific to the N-terminal conserved part also recognize the cell surface of E. cuniculi and E. intestinalis. In contrast, sera raised against the C-terminal domains of E. hellem SWP1s do not cross-react with E. cuniculi and E. intestinalis. Mouse anti-SWP1 antisera were used at a 1:100 dilution. The secondary antibody was Alexa 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG at a 1:1,000 dilution. Bars, 3 μm.