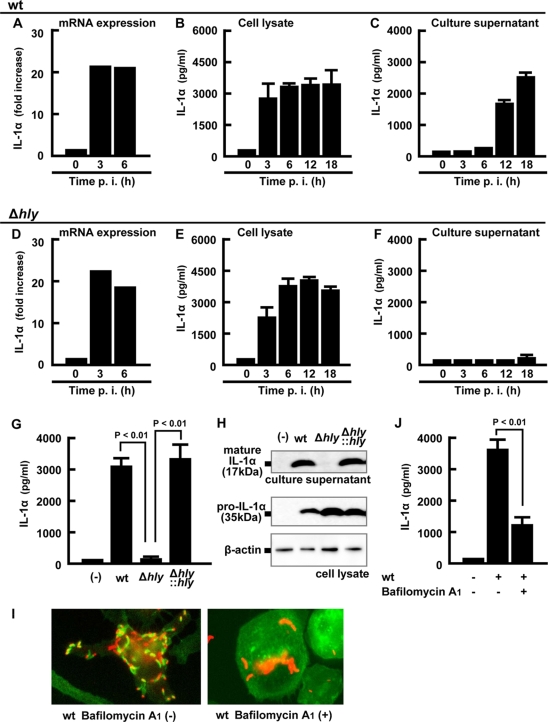
FIG. 2.
LLO-dependent entry into the cytoplasm is required for the secretion of IL-1α. Macrophages were infected with the wt (A to C) or Δhly strain (D to F) for 1 h, and total cellular RNA, the cell lysate, and the culture supernatant were prepared at the indicated time points. Expression of IL-1α mRNA was quantified by real-time RT-PCR (A and D). The levels of mature IL-1α in the cell lysates (B and E) and the culture supernatants (C and F) were determined by ELISA. Macrophages were infected with the wt, Δhly, or hly-complemented (Δhly::hly) strain for 1 h and cultured for 18 h in the presence of gentamicin. The amount of mature IL-1α in the culture supernatant and pro-IL-1α in the cell lysate was quantified by ELISA (G) and Western blotting (H). β-Actin is utilized as a loading control. Macrophages were treated with 0.5 μM bafilomycin A1 for 30 min and infected with L. monocytogenes for 5 h, fixed, and stained with rabbit anti-L. monocytogenes antibody (Ab), Alexa Fluor 594-anti-rabbit IgG Ab, and Alexa Fluor 488-phalloidin. L. monocytogenes (red) and F-actin (green) are visualized using fluorescence microscopy. L. monocytogenes associating with F-actin represents a bacterium that has escaped from a phagosome (I). Macrophages were treated with 0.5 μM bafilomycin A1 for 30 min, infected with L. monocytogenes for 1 h, and cultured for 18 h in the presence of gentamicin. The supernatant was collected, and the IL-1α concentration was determined by ELISA (J). Three independent experiments were done, and similar results were obtained. (−), no infection.