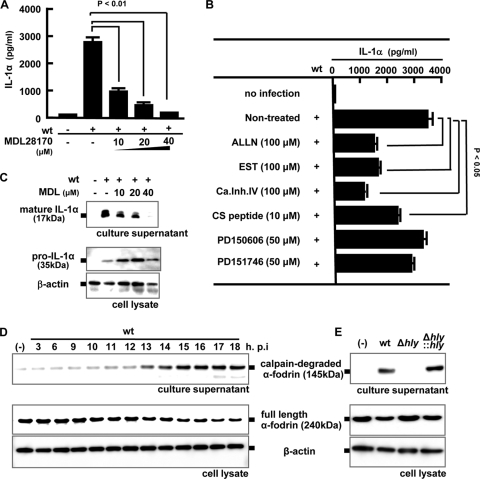
FIG. 5.
Involvement of calpain activation in the processing and secretion of IL-1α. Macrophages were infected with the wt (MOI = 5), and MDL28170 (MDL) was added to the culture 3 h later at the indicated concentrations. Macrophages were then cultured for 18 h, and the IL-1α level in the culture supernatant was determined by ELISA (A). The amounts of mature IL-1α in the culture supernatant and pro-IL-1α in the cell lysate were determined by Western blotting (B). Macrophages were infected with the wt for 1 h, and other calpain inhibitors (ALLN, EST, calpain inhibitor IV, CS peptide, PD150606, and PD151746) were added 3 h after infection. Cells were further cultured for 15 h, and mature IL-1α production in the culture supernatant was measured by ELISA (C). Macrophages were infected with the wt at a MOI of 5 for 1 h and cultured in the presence of gentamicin for the indicated periods. The full-length form and the proteolytic fragment of α-fodrin were detected by Western blotting in the cell lysate and the culture supernatant, respectively (D). The activity of calpain was monitored by measuring the amount of degraded fragment of α-fodrin. β-Actin was utilized as a loading control. Similarly, macrophages were infected with the wt, Δhly, or Δhly::hly strain for 1 h. Eighteen h after infection, Western blotting was performed to evaluate the activity of calpain (E). Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. (-), no infection.