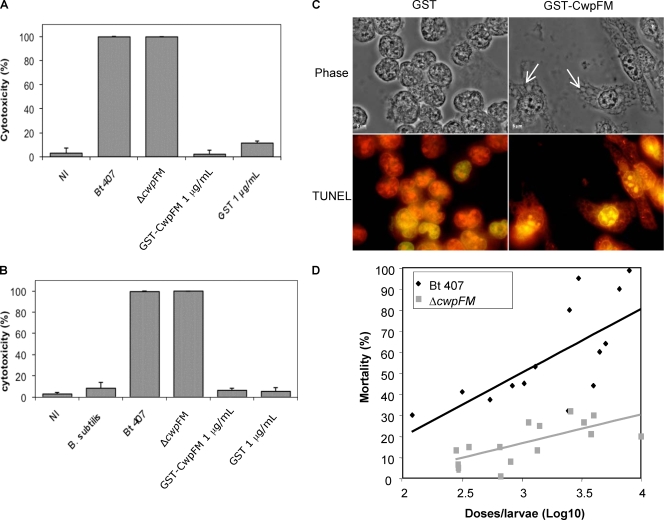
FIG. 2.
(A and B) Evaluation of cytotoxicity using trypan blue dye. HeLa (A) or macrophage (B) cells (1 × 105) were incubated with the culture supernatant of B. thuringiensis 407, the cwpFM mutant, or B. subtilis, or with purified GST-CwpFM (1 μg/ml). Control cells were either noninfected (NI) or incubated with purified GST (1 μg/ml). After 2 h of incubation, cell mortality was evaluated by trypan blue dye exclusion. (C) CwpFM induces vacuolization of macrophages. Macrophages (106 cells/well) were incubated with 1 μg/ml of purified GST-CwpFM or GST. After treatment, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 25 min at 4°C. Cell morphology was observed under a phase-contrast microscope (100× objective; Leica) (top panels). Arrows indicate cell vacuoles. Alternatively, cells were stained using the DeadEnd fluorometric TUNEL kit and observed under a fluorescence microscope (bottom panels). All cells are labeled in red, and potential apoptotic cells are stained green. Images are representative of at least three independent experiments. (D) CwpFM virulence against G. mellonella larvae. Various concentrations of wild-type and cwpFM strains were inoculated into the hemocoel of three groups of 20 G. mellonella larvae. Mortality was recorded after 24 h at 37°C, and the LD50 was determined using the probit method.