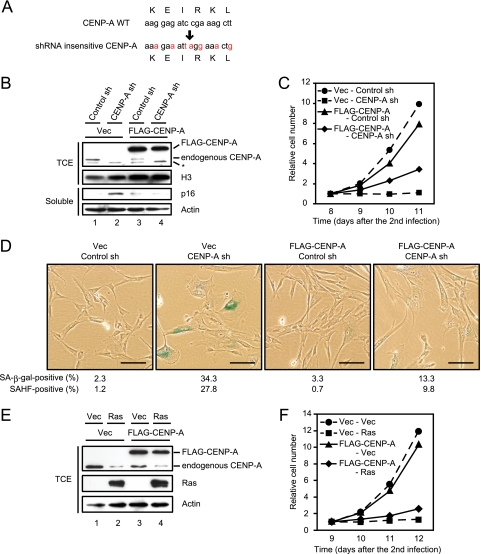
FIG. 5.
The expression of FLAG-tagged shRNA insensitive CENP-A rescues senescencelike phenotypes caused by shRNA to CENP-A. (A) A mutated shRNA cleavage site in an shRNA insensitive CENP-A cDNA is shown. (B) Immunoblotting of TIG3 cells expressing vector control (Vec) or FLAG-tagged shRNA insensitive CENP-A (FLAG-CENP-A) (first infection) in combination with control or CENP-A shRNA (second infection). TCE and soluble proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Histone H3 and actin were used as loading controls. Bands labeled with an asterisk are nonspecific proteins detected by anti-CENP-A antibody. (C) Growth curves of the cells indicated in panel B. The number of cells on day 8 after infection was set at 1. The data are means from two independent experiments. (D) SA-β-Gal staining performed on day 10 after the second infection. The proportions of SA-β-Gal-positive (n = 300) and SAHF-positive cells (n = 300) are shown. Scale bars, 100 μm. (E) Immunoblotting of TIG3 cells expressing vector control (Vec) or FLAG-CENP-A (first infection) in combination with vector control (Vec) or Ras (second infection). TCE were resolved by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Actin was used as a loading control. (F) Growth curves of the cells indicated in panel E. The number of cells on day 9 after infection was set at 1. The data are means from two independent experiments.