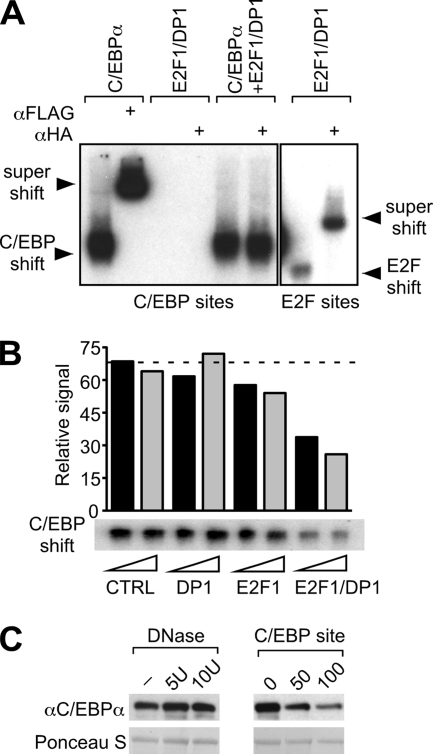
FIG. 6.
E2F-DP disrupts C/EBPα binding to its consensus DNA sites. (A) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay using radiolabeled probes containing either a C/EBP-binding site (left panel) or an E2F consensus binding site (right panel). Nuclear extracts of 293T cells, transfected with FLAG-C/EBPα and/or HA-E2F1/DP1 expression constructs, were incubated with probes and with anti-FLAG or anti-HA antibodies, as indicated. Binding and supershift are shown on this representative autoradiogram. (B) DNA binding of C/EBPα in the presence of purified E2F1 and DP1 proteins. GST-DP1 or GST-E2F1 fusion proteins were bound to GST beads and detached from the GST tag by thrombin digestion, resulting in the elution of DP1 or E2F1 proteins. In vitro-translated FLAG-C/EBPα was preincubated with increasing amounts (triangle) of DP1, E2F1, E2F1-DP1, or control (CTRL, GST alone) eluate. When DP1 or E2F1 eluate was added separately, it was combined with control eluate to maintain equal protein amounts. Binding of C/EBPα to a radiolabeled C/EBP probe was examined by gel shift assay and detected by autoradiography. The bar graph represents the signal quantification of the autoradiogram. The dashed line is set up at the CTRL level. (C) DNA competes with interaction between C/EBPα and E2F1. Binding of C/EBPα expressed in 293T cells (input) to E2F1 (GST fusion proteins) was examined in a GST pulldown assay under conditions of DNA depletion (DNase treatment) or addition of DNA (C/EBP-binding site). In the left panel, E2F1-C/EBPα binding reactions were incubated in the presence of 5, 10, or 10 U of heat-inactivated DNase (−). In the right panel, 0, 50, or 100 ng of C/EBP probe was added to the C/EBPα-E2F1 binding reactions. Bound proteins were detected and quantified by immunoblotting and pulldown of GST proteins controlled by Ponceau S staining.