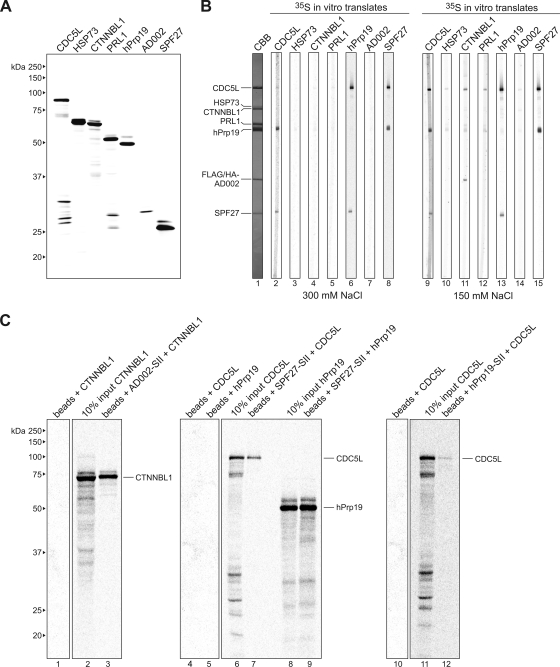
FIG. 6.
Far-Western and coimmunoprecipitation analyses reveal additional interactions between components of the hPrp19/CDC5L complex. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of in vitro-translated 35S-labeled proteins (as indicated above each lane). Proteins were visualized by autoradiography. The molecular masses of marker proteins are indicated on the left. (B) Far-Western overlay analysis of protein-protein interactions between individual hPrp19/CDC5L complex proteins. SDS-PAGE-separated hPrp19/CDC5L complex proteins were blotted onto nitrocellulose strips and visualized by staining with Coomassie blue (CBB; lane 1) or were incubated with 35S-labeled, in vitro-translated hPrp19/CDC5L complex proteins in buffer containing 300 mM (lanes 2 to 8) or 150 mM (lanes 9 to 15) NaCl and visualized by autoradiography (lanes 2 to 15). hPrp19/CDC5L complex proteins are indicated on the left. (C) Coimmunoprecipitation confirms interactions between SPF27 and both CDC5L and hPrp19, between CTNNBL1 and AD002, and between CDC5L and hPrp19. In vitro-translated 14C-labeled CTNNBL1, CDC5L, and hPrp19, as indicated above each lane, were incubated alone (lanes 1, 4, 5, and 10) or with StrepII (SII)-tagged AD002 (lane 3), SPF27 (lanes 7 and 9), or hPrp19 (lane 12), and pulldowns were subsequently performed with Strep-Tactin Sepharose beads. Coprecipitated proteins or 10% of the input (lanes 2, 6, 8, and 11) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and visualized by autoradiography. The presence of the StrepII-tagged protein was confirmed by Coomassie blue staining (data not shown). The identities of the coprecipitated proteins are indicated on the right.