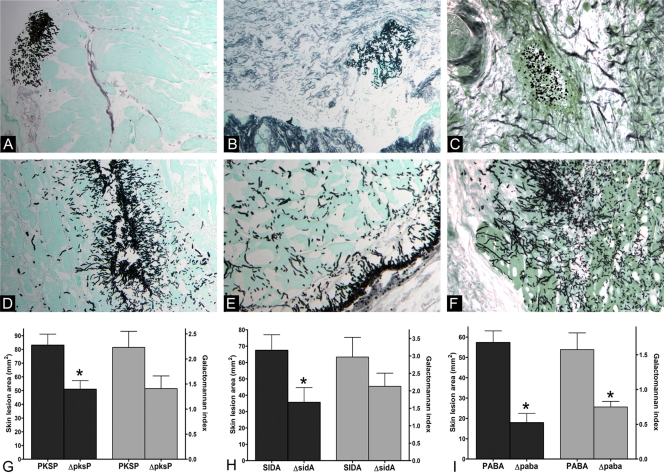
FIG. 3.
Features of murine thigh infection with hypovirulent A. fumigatus mutants and their parental wild-type strains. (A to F) GMS-stained thigh tissue sections of mice infected with A. fumigatus isolates with deletion mutations in known virulence-associated genes and parental wild-type strains are shown (original magnification, ×200). (A to C) In tissue infected with the ΔpksP, ΔsidA, and ΔpabaA mutants, fungal elements were few, clustered, and limited to subcutaneous tissue. (C) ΔpabaA conidia failed to germinate. (D to F) In contrast, the parental wild types produced widespread infection with deep invasion of muscle tissue. (G to I) The corresponding differences in skin lesion areas (black bars) and tissue galactomannan content (gray bars) are shown. Bars and error bars represent means and standard errors, respectively (15 mice per A. fumigatus strain). *, P < 0.05.