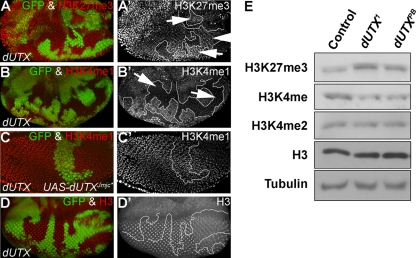
FIG. 2.
dUTX controls H3K27me3 demethylation and H3K4 monomethylation. (A to D) Eye imaginal discs were labeled with antibodies specific for the indicated histone methyl modification. GFP fluorescence was used to identify dUTX clones. Left panels are the merged GFP and antibody channels. Right panels are the antibody-only channels. To ease the identification of dUTX clones, clonal boundaries are indicated with white lines. (A and A′) Global levels of H3K27me3 are increased in dUTX mutant clones (arrows) in eye imaginal discs. dUTX mutant clones are negatively marked by the absence of GFP. (B and B′) Global levels of H3K4me1 are reduced in dUTX mutant clones (arrows) in eye imaginal discs. dUTX mutant clones are negatively marked by the absence of GFP. (C and C′) Expression of the JmjC catalytic mutant dUTXJmjC* in dUTX mutant clones by the MARCM system rescues the H3K4me1 methylation defect. Clones are positively marked by GFP. (D and D′) Global levels of histone H3 are not altered in dUTX mutant clones in eye imaginal discs. dUTX mutant clones are negatively marked by the absence of GFP. (E) Western blot analysis of larval extracts of the indicated genotype probed with the antibodies listed at the left. Genotypes are as follows: ey-FLP; dUTX1 FRT40A/P[ubi-GFP] FRT40A (A, B, and D) and hs-FLP UAS-CD8:GFP; dUTX1 FRT40A UAS-dUTXJmjC*/P[tub-GAL80] FRT40A/P[tub-GAL4] (C).