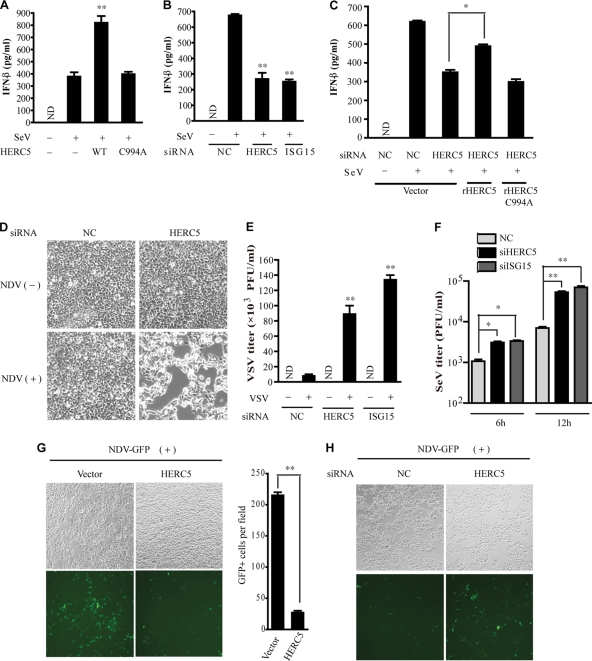
FIG. 7.
HERC5 modulates IRF3-mediated antiviral responses. (A and B) HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids (50 ng) (A) or siRNAs (B). Six hours after SeV infection, IFN-β production was determined by ELISA. (C) The indicated siRNAs were transfected into HEK293 cells in the presence or absence of siRNA-resistant HERC5. Six hours after SeV infection, IFN-β production was determined by ELISA. (D) HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs. Twenty-four hours posttransfection, the cells were infected with NDV for an additional 20 h. The cytopathic effects (CPE) were observed by differential interference contrast DIC microscopy. Original magnification, ×100. (E) HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs. Twenty-four hours posttransfection, the cells were infected with SeV for an additional 10 h. Equal amounts of the culture supernatants (approximately 100 μl) were applied to fresh HEK293 cells for 6 h, followed by VSV infection. The titers of VSV were determined by a standard plaque assay. (F) HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs. Twenty-four hours posttransfection, the cells were infected with SeV for different times. Equal amounts of the conditioned medium with anti-IFN-α/β (20 μg/ml) were applied to Vero cells. A plaque assay for SeV was carried out using Vero cells as described previously. (G and H) NDV-GFP replication in HEK293 cells transfected with exogenous HERC5 (G) or HERC5 siRNA (H) was visualized by fluorescence microscopy. Original magnification, ×100. GFP-positive cells were quantified (G, right). Data are presented as means ± SD (n = 3 replicates). ND, not detected. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.