FIG. 2.
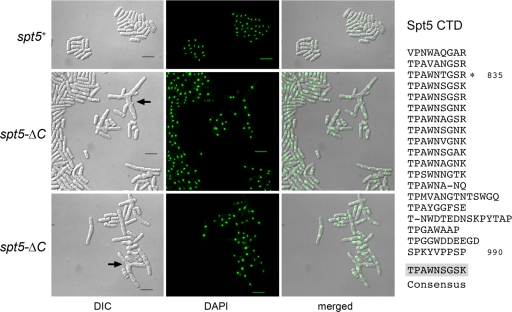
Deletion of the Spt5 CTD results in aberrant cell morphology. The amino acid sequence of the Spt5 CTD is displayed at right, with the nonamer repeats aligned vertically. The consensus sequence TPAWNSGSK is shown below the alignment. Previously it was shown that truncation of the CTD to amino acid 835, leaving three nonamer repeats, had no apparent impact on cells growth. In the present study, the entire CTD was deleted in the spt5-ΔC strains of S. pombe. Cell morphology and nuclear DNA localization were assessed by light microscopy. spt5+ and spt5-ΔC cells were cultured in YES medium at 30°C. Exponentially growing cells were fixed in 70% ethanol, treated with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI), and then visualized by differential interference contrast (DIC) and fluorescence (DAPI) microscopy (Nikon Eclipse E600 microscope equipped with a Spot camera). The bars in the DIC images are 10 μm. The arrows denote branched cells.