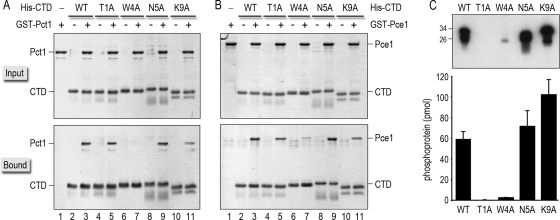
FIG. 5.
Effects of Spt5 CTD-Ala mutations on binding to capping enzymes and on CTD phosphorylation by Cdk9. (A and B) Binding of GST-tagged Pct1 (A) or Pce1 (B) to wild-type and Ala-substituted His10-Smt3-Spt5-CTD proteins was assessed by Ni-agarose affinity chromatography as described in Materials and Methods. The input proteins are specified above the lanes by “+.” Aliquots comprising 10% of the input material (top panels) and 30% of the bead-bound material (bottom panels) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Polypeptides were visualized by staining the gels with Coomassie blue dye. (C) Kinase reaction mixtures (20 μl) containing 50 mM Tris acetate (pH 6.0), 1 mM DTT, 2.5 mM MnCl2, 50 μM [γ32P]ATP, ∼100 ng of recombinant Cdk9T212E/Pch1 kinase (36), and 1 μg of recombinant His10-Smt3-Spt5-CTD phosphoacceptor as specified were incubated for 1 h at 20°C. The reactions were quenched by adding SDS to a 1% final concentration. Aliquots (3 μl) of the reaction mixtures were then analyzed by 12% SDS-PAGE. The 32P-labeled proteins were visualized by autoradiography of the dried gel (top panel). The positions and sizes (kDa) of marker polypeptides are indicated on the left. The extents of label transfer from [γ32P]ATP to His10-Smt3-Spt5-CTD were quantified by scanning the gel with a Molecular Dynamics Typhoon PhosphorImager. The data were normalized to the initial reaction volume and are plotted as a bar graph in the bottom panel. Each datum is the average of results from three or four separate experiments ± SD.