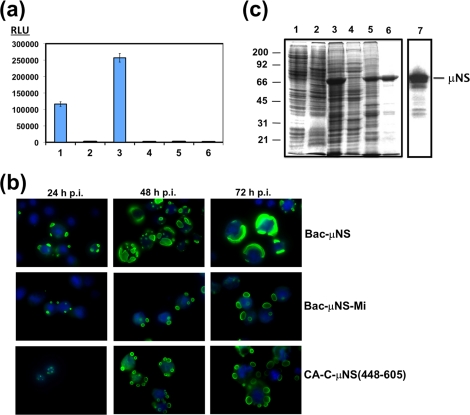
FIG. 2.
Mammalian two-hybrid analysis, and baculovirus expression of μNS-derived constructs in insect cells. (a) Mammalian Matchmaker two-hybrid analysis of μNS self-interaction. The bars represent the luciferase levels of extracts from Cos-7 cells transfected with the following plasmid combinations: 1, positive control included in the system (see Materials and Methods); 2, empty plasmids expressing activation and DNA-binding domains plus the luciferase reporter plasmid; 3, plasmids expressing μNS fused to the activation and DNA-binding domains plus luciferase reporter plasmid; 4, plasmids expressing μNS fused to the activation domain and empty plasmid expressing the DNA-binding domain plus luciferase reporter plasmid; 5, empty plasmid expressing the activation domain and plasmid expressing μNS fused to the DNA-binding domain plus luciferase reporter plasmid; 6, untransfected cells. RLU are indicated on the left. The error bars indicate standard deviations. (b) Time course analysis showing the subcellular localization of μNS, μNS-Mi, and CA-C-μNS(448-605) proteins in Sf9 cells. The last two proteins are described in Fig. 5 and 7, but they are included here for comparison. Semiconfluent monolayers of Sf9 cells were infected with a recombinant baculovirus expressing μNS (top), μNS-Mi (middle), or CA-C-μNS(448-605) (bottom). The cells were then fixed and immunostained with rabbit antibodies raised against μNS, followed by Alexa 488-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (green), at the infection times indicated above the images. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). (c) Expression, purification, and immunoblot analysis of μNS-derived inclusions. Sf9 insect cells infected with a recombinant baculovirus expressing μNS were lysed in hypotonic buffer at 72 h p.i., and the resulting cell extract (lane 3) was fractionated by centrifugation into pellet and supernatant fractions (the supernatant fraction is shown in lane 4). The pellet was then washed twice with hypotonic buffer, resuspended in the same volume of hypotonic buffer, and sonicated. The sonicated extract (lane 5) was centrifuged, and the pelleted inclusions were washed five times with hypotonic buffer (lane 6). Mock-infected and wild-type-baculovirus-infected Sf9 cell extracts, obtained by lysing the cells in hypotonic buffer at 72 h p.i., are shown in lanes 1 and 2, respectively. All samples were resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the protein bands were visualized by Coomassie blue staining. The position of recombinant μNS is indicated on the right and those of the molecular weight markers on the left. The sample in lane 6 (purified μNS inclusions) was subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-μNS antibodies (lane 7).