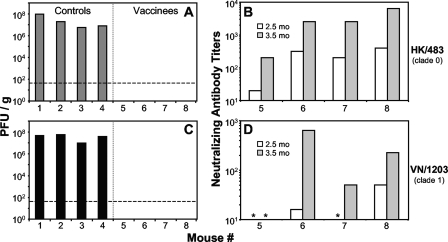
FIG. 3.
VSV-based vaccines provide sterilizing immunity against heterologous AIVs. Mice (n = 4) were vaccinated with the first position H5 HA vectors (vaccinees) (A and C) or negative-control vectors (controls) (A and C) and challenged with either HK/483 (A and B) or VN/1203 (C and D) as in Fig. 2. (C to F) At 3 days postchallenge, the lungs were harvested, and the virus titer was determined by plaque assay. No virus was detected in any vaccinee homogenate. The limit of detection for this assay was ≤50 PFU/g (dashed line) where the average lung mass was 100 mg. (B and D) Sera collected from vaccinated mice (mouse 5 to mouse 8) at 2.5 months postprime (preboost; white bars) or 1 month postboost (3.5 months postprime; gray bars) were subjected to a microneutralization assay (39) against the challenge virus (HK/483 [B] and VN/1203 [D]). All mice vaccinated with the negative-control vectors (mouse 1 to mouse 4) had undetectable nAb activity, which corresponds to a titer of 10 in this assay (data not shown). Asterisks indicate sera from H5 HA-vaccinated animals with no detectable nAb.