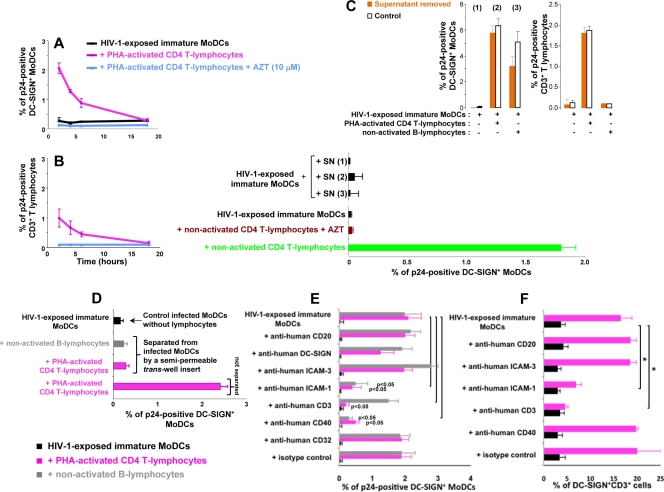
FIG. 4.
Early cell-to-cell contact is required for the increase in HIV-1 replication in infected DCs. (A and B) CD4 T lymphocytes were added at various time points after the infection of immature MoDCs. The percentage of DC-SIGN+ DCs (A) or CD3+ CD4 T lymphocytes (B) expressing p24 was determined after 48 h. (C) Supernatants (SN) from HIV-1-exposed MoDCs, cultured alone [SN (1)] or cocultured with CD4 T lymphocytes [SN (2)] or B lymphocytes [SN (3)], were collected at 6 h and added to infected immature MoDCs. (Bottom) After 48 h, intracellular p24 levels were determined. (Top) In parallel, we used flow cytometry to measure intracellular p24 production at 48 h in cells from which supernatants (1, 2, and 3) had been removed (orange bars) or not removed (white bars). (D) HIV-1-exposed MoDCs and uninfected lymphocytes were left in contact or separated with a Transwell insert, and intracellular p24 levels were determined after 48 h. (E) PHA-activated CD4 T or B lymphocytes were pulsed with 20 μg/ml mouse monoclonal IgG2a directed against human CD3 (clone OKT3 [azide free]; Miltenyi Biotec) before being added to HIV-1-exposed immature MoDCs. We added 20 μg/ml mouse monoclonal IgG1 directed against CD40 (clone B-B20 [azide free]; Abcam), ICAM-3 (clone B-R1 [azide free]; Abcam), ICAM-1 (clone 1H4 [azide free]; Abcam), CD20 (clone MEM-97 [azide free]; Abcam), DC-SIGN (clone DCN46; BD Pharmingen), CD32 (clone 3D3; BD Pharmingen), or a mouse monoclonal IgG1 isotype (clone NCM1; Abcam) to the coculture at the same time as CD4 T lymphocytes. After 48 h of coculture, intracellular p24 levels were determined by flow cytometry. (F) In parallel, MoDC-CD4 T-cell conjugates were evaluated by determining the percentage of DC-SIGN+ CD3+ cells by flow cytometry. The values plotted on all graphs are means ± SD of triplicate results from a single representative experiment. A value of P of <0.05 was considered significant. *, P < 0.05 versus the corresponding control group.