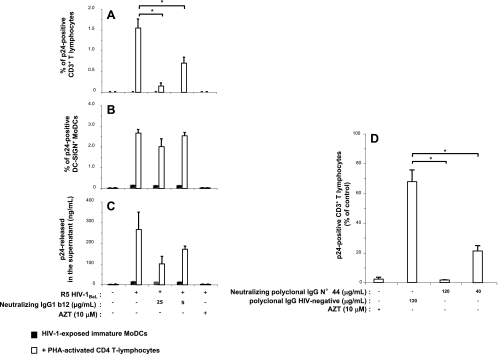
FIG. 5.
Neutralizing activities of anti-HIV-1 monoclonal or polyclonaI IgGs toward the trans-infection of CD4 T lymphocytes. Monoclonal neutralizing IgG1b12 (A, B, and C) or polyclonal neutralizing IgG preparation no. 44 (D) was added, together with activated CD4 T lymphocytes, to HIV-1-exposed immature MoDCs. After 48 h of coculture, intracellular and extracellular p24 production levels were determined by flow cytometry and p24 ELISA, respectively. Shown are the percentages of p24-positive primary CD3+ CD4 T lymphocytes (A and D) and of p24-positive DC-SIGN+ MoDCs (B) and amounts of viral p24 released into the supernatant (C) when HIV-1-exposed immature MoDCs were cultured with or without activated CD4 T lymphocytes in the presence or absence of neutralizing IgGs or AZT. The values shown are the means ± SD of triplicate results. Purified neutralizing polyclonal IgGs were obtained from the serum of HIV-1-positive asymptomatic patient no. 44, and nonneutralizing polyclonal IgGs were obtained from a pool of sera from HIV-1-negative healthy donors. A value of P of <0.05 was considered significant. *, P < 0.05 versus the corresponding control group.