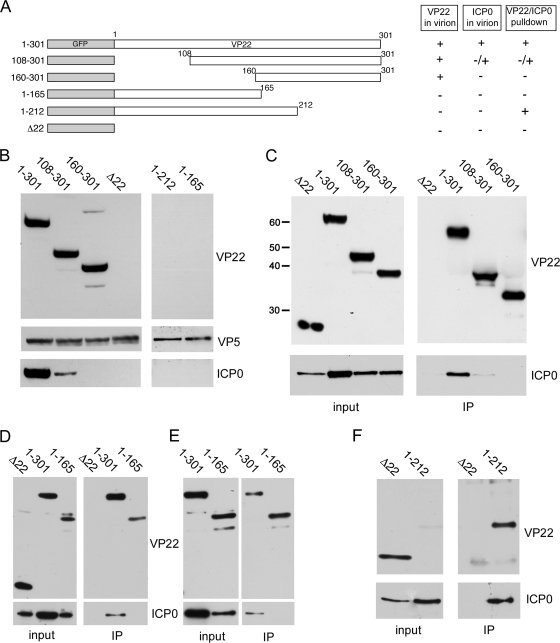
FIG. 4.
The N terminus of VP22 is required for ICP0 assembly into the virion. (A) Line drawing of the VP22 truncation mutants used in this study. (B) Equivalent amounts of virions from the viruses described in the legend for panel A were analyzed by Western blotting for VP22, VP5, and ICP0. (C) Immunoprecipitations using a polyclonal GFP antibody were carried out on Vero cells infected with HSV-1 expressing full-length GFP-22 (1 to 301), the two N-terminal VP22 truncation mutants (108 to 301 and 160 to 301), or GFP in place of VP22 (Δ22), 20 h after infection at a multiplicity of infection of 1. The resulting complexes were analyzed by Western blotting for the C terminus of VP22 or ICP0. The sizes of the molecular weight markers (in thousands) are indicated on the left. (D and E) As described in the legend for panel C, using cells infected with HSV-1 expressing full-length VP22 (1 to 301), the N-terminal half of VP22 (1 to 165), or GFP in place of VP22 (Δ22). Western blots were carried out using antibodies for the N terminus of VP22 or ICP0. (F) As described in the legend for panel D, using cells infected with HSV-1 expressing GFP in place of VP22 (Δ22) or the C-terminal truncation (1 to 212).