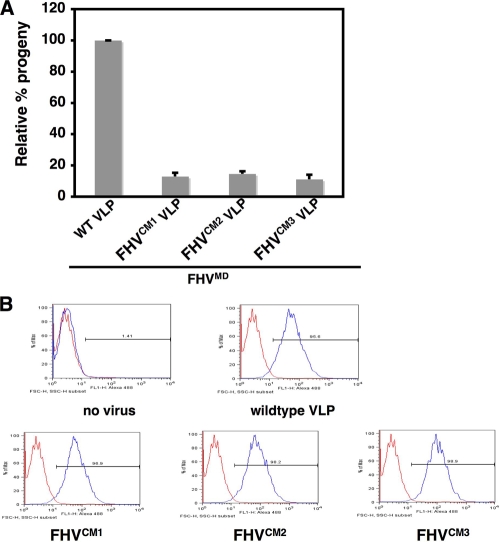
FIG. 5.
Calcium-site-mutated VLPs bind to DL-1 cells but cannot rescue the infectivity of maturation-defective FHV. (A) Progeny virus produced by coinfecting 1 × 108 Drosophila DL-1 cells with 1.5 × 103 particles/cell of D75N/N363T FHV and 9 × 103 particles/cell of wild-type VLPs or each of the mutated VLPs. [35S]methionine-cysteine-labeled progeny virus was quantified, with the amount of progeny produced during coinfection with D75N/N363T FHV and wild-type VLPs normalized at 100%. (B) FACS analysis of the binding of wild-type or mutated VLPs to 1 × 106 Drosophila DL-1 cells for 1 h at 4°C. Bound particles were detected using a rabbit polyclonal primary antibody against FHV capsid protein and a goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody conjugated with Alexa 488 (Molecular Probes). Five percent BSA was added to cells as a negative control, followed by antibody incubations. Data shown are representative of two separate experiments.