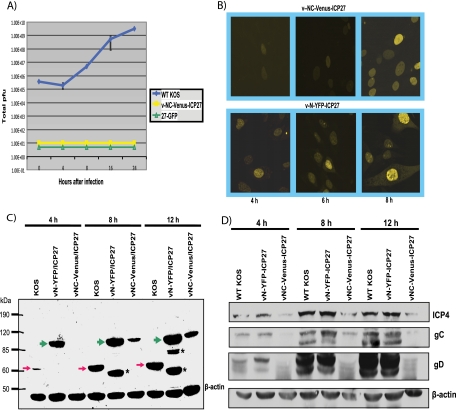
FIG. 6.
Recombinant virus v-NC-Venus-ICP27 is defective in viral replication. The v-NC-Venus-ICP27 virus was constructed by the marker transfer of N-Venus/ICP27/C-Venus into 27-LacZ (40), replacing the 27-LacZ locus. (A) One-step growth curves were performed by infecting Vero cells with KOS, 27-GFP, and vNC-Venus-ICP27 at an MOI of 1. The experiments were performed in triplicate, and viral titers at 4, 8, 16, and 24 h were determined by plaque assays on Vero cells. (B) Vero cells were infected with v-NC-Venus-ICP27 and v-N-YFP-ICP27 at an MOI of 10. Venus and YFP fluorescence were visualized directly on living cells at 4, 6, and 8 h after infection. (C) Vero cells were infected with KOS, v-N-YFP-ICP27, and v-NC-Venus-ICP27 at an MOI of 10. Western blot analysis was performed on protein samples isolated at 4, 8, and 12 h after infection. The blot was probed with anti-ICP27 and anti-GFP antibodies and with β-actin antibody as a loading control. The red arrows indicate the position of wild-type ICP27. The green arrows indicate the position of N-YFP-ICP27 and N-Venus/ICP27/C-Venus. The asterisks denote ICP27 protein degradation products in the N-YFP-ICP27 lanes. The position of molecular size markers is shown to the left of the gel. (D) Vero cells infected with KOS, vN-YFP-ICP27, and v-NV-Venus-ICP27 at an MOI of 10 were harvested at 4, 8, and 12 h after infection, and Western blot analysis was performed as described previously (42). The blots were probed with antibodies directed to ICP4, gC, gD, and β-actin as a loading control.