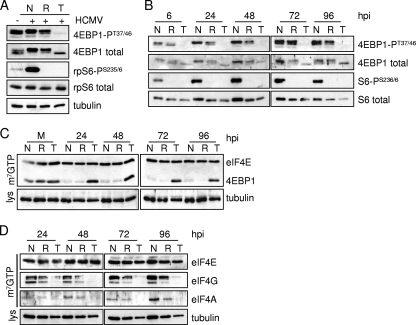
FIG. 4.
Rapamycin-resistant mTOR activity is required for 4EBP1 phosphorylation and eIF4F complex integrity during HCMV infection. Serum-starved confluent human fibroblasts were infected with HCMV at a multiplicity of 3 PFU/cell. At 1 hpi, cultures were treated with the vehicle in which drugs were dissolved (N) (DMSO), rapamycin (R) (20 nM), or Torin1 (T) (250 nM). (A) At 48 hpi the phosphorylation status of mTORC1 targets was assessed by Western blot assay by using antibodies to phosphorylated targets (4EBP1-PT37/46 and rpS6-PS235/6) and total proteins. Tubulin was assayed as a loading control. (B) Same as above (A) except that cells were harvested at the indicated times. (C and D) After mock infection (M) or infection with HCMV (WT) at a multiplicity of 3 PFU/cell, cultures were harvested at the indicated times. Equivalent amounts of protein from each sample were incubated with m7GTP-Sepharose, and the isolated protein complexes were analyzed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies to the eIF4F complex and 4EBP1. In all cases the results are representative of at least two independent experiments. lys, lysate.