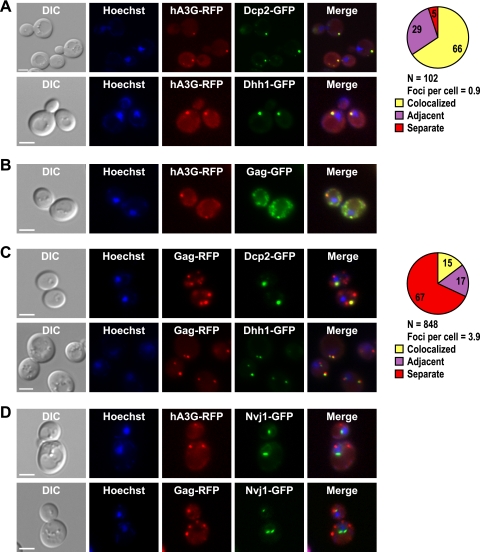
FIG. 1.
Human A3G and Ty1 Gag localize to P bodies. Individual yeast cells treated with Hoechst dye (Hoechst) to visualize cell nuclei were located by differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy and fluorescence microscopy. Scale bar, 3 μm. Fluorescent images were merged using Adobe Photoshop. (A) Yeast strains harboring DCP2-GFP or DHH1-GFP and plasmid pGAL1-A3G-RFP were grown in galactose-containing broth, and live cells were visualized to determine the subcellular locations of P bodies and A3G-RFP and their joint subcellular location (Merge). The pie graph shows the percentage of A3G-RFP foci that colocalize with Dcp2-GFP foci or were adjacent to Dcp2-GFP foci (see Materials and Methods for complete description of quantitation). “N” represents the total number of A3G-RFP foci examined for colocalization with Dcp2-GFP. (B) Live cells harboring the chromosomal Ty1-GFP-3566 element and the pGAL1-A3G-RFP plasmid were grown in the presence of galactose to determine the subcellular locations of Gag-GFP and A3G-RFP. (C) Live cells harboring DCP2-GFP or DHH1-GFP and plasmid pLTR-GAG-RFP were visualized to determine the subcellular locations of P bodies and Ty1 Gag-RFP and their joint subcellular location. The pie graph shows the percentage of Gag-RFP foci that colocalize or are adjacent to Dcp2-GFP foci. “N” represents the number of Gag-RFP foci examined for colocalization with Dcp2-GFP. (D) The subcellular locations of Gag-RFP and A3G-RFP were visualized in live cells harboring NVJ1-GFP and plasmid pGAL1-A3G-RFP or pLTR-Gag-RFP. NVJ1 encodes a nuclear-vacuolar junction protein.