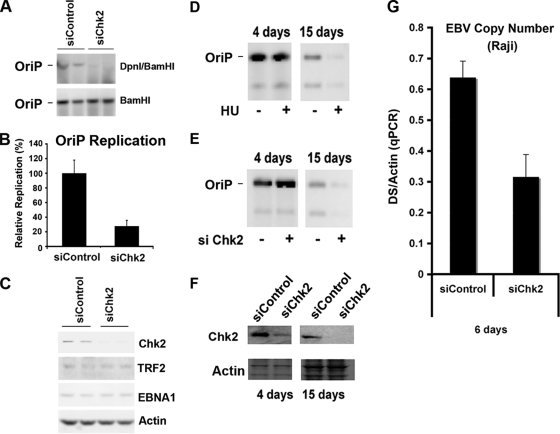
FIG. 1.
Chk2 depletion inhibits OriP DNA replication and plasmid maintenance. (A) HCT116 cells were cotransfected with siControl or siChk2 siRNA and with OriP plasmid-coexpressing EBNA1 and assayed for transient DNA replication. Plasmid DNA, shown in duplicates, was digested with BamHI (bottom) or DpnI plus BamHI (bottom) and visualized by Southern blotting. (B) Replication efficiency was quantified for at least three independent transfections as the ratio of resistant DpnI to total plasmid DNA recovered (BamHI-linearized DNA), and replication for siCon was normalized to 100%. (C) Western blot control to assay siChk2 depletion and EBNA1, TRF2, and actin expression levels in cells shown in A. (D) HeLa cells were selected for GFP-expressing OriP plasmids and then treated with (+) or without (−) HU (50 μM) for 4 or 15 days, as indicated. OriP plasmids were then extracted from the same number of cells and assayed by Southern blotting. (E) Same as above (D) except that cells were transfected with control or Chk2-targeting siRNA every 3 days for 4 or 15 days. No HU was included in these experiments. (F) The siRNA-transfected cells shown in E were analyzed by Western blotting for Chk2 (top) or actin (bottom) at 4 and 15 days after transfection of the OriP plasmid, as indicated. (G) Raji cells were nucleofected with siRNA for Chk2 or control siRNA every third day for 6 days. The EBV genome copy number was measured by real-time PCR analysis of the EBV DS region relative to cellular actin DNA. qPCR, quantitative PCR.