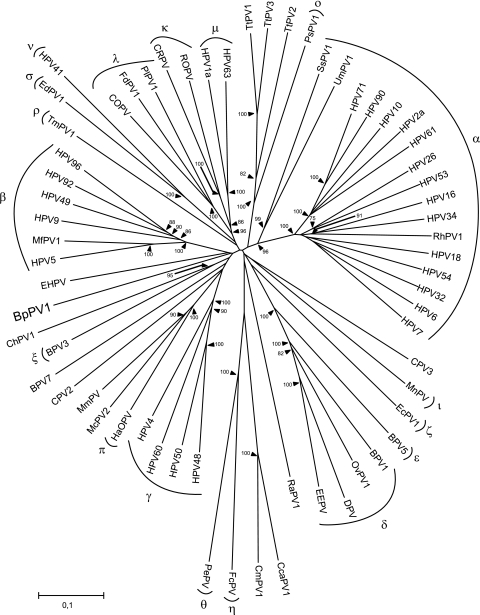
FIG. 2.
Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree, based on a combined concatenated E1/E2/L2/L1 nucleotide sequence alignment of BpPV1 and 62 other PVs, using only the 1st and 2nd codon positions. The PV types were, in the genus Alphapapillomavirus, HPV32 (GenBank accession number NC_001586), HPV10 (NC_001576), HPV61 (NC_001694), HPV2a (NC_001352), HPV26 (NC_001583), HPV53 (NC_001593), HPV18 (NC_001357), HPV7 (NC_001595), HPV16 (NC_001526), HPV6 (NC_001355), HPV34 (NC_001587), rhesus PV type 1 (RhPV1; NC_001678), HPV54 (NC_001676), HPV90 (NC_004104), and HPV71 (AY330621); in the genus Betapapillomavirus, HPV5 (NC_001531), HPV9 (NC_001596), HPV49 (NC_001591), HPV92 (NC_004500), HPV96 (NC_005134), and Macaca fascicularis PV type 1 (MfPV1; EF028290); in the genus Gammapapillomavirus, HPV4 (NC_001457), HPV48 (NC_001690), HPV50 (NC_001691), and HPV60 (NC_001693); in the genus Deltapapillomavirus, European elk PV (EEPV; NC_001524), deer PV (DPV; NC_001523), ovine PV type 1 (OvPV1; NC_001789), and BPV1 (NC_001522); in the genus Epsilonpapillomavirus, BPV5 (NC_004195); in the genus Zetapapillomavirus, Equus caballus PV type 1 (EcPV1; NC_003748); in the genus Etapapillomavirus, Fringilla coelebs PV (FcPV; NC_004068); in the genus Thetapapillomavirus, Psittacus erithacus timnesh PV (PePV; NC_003973); in the genus Iotapapillomavirus, Mastomys natalensis PV (MnPV; NC_001605); in the genus Kappapapillomavirus, cottontail rabbit PV (CRPV; NC_001541) and rabbit oral PV (ROPV; NC_002232); in the genus Lambdapapillomavirus, COPV (NC_001619), Felis domesticus PV type 1 (FdPV1; NC_004765), and Procyon lotor PV type 1 (PlPV1; NC_007150); in the genus Mupapillomavirus, HPV1 (NC_001356); in the genus Nupapillomavirus, HPV41 (NC_001354); in the genus Xipapillomavirus, BPV3 (NC_004197); in the genus Omicronpapillomavirus, Phocoena spinipinnis PV type 1 (PsPV1; NC_003348); in the genus Pipapillomavirus, hamster oral PV (HaOPV; E15111); in the genus Rhopapillomavirus, Trichechus manatus latirostris PV type 1 (TmPV1; NC_006563); in the genus Sigmapapillomavirus, Erethizon dorsatum PV type 1 (EdPV1; NC_006951); and unclassified types Rousettus aegyptiacus PV type 1 (RaPV1; NC_008298), BPV7 (NC_007612), canine PV type 2 (CPV2; NC_006564), CPV3 (NC_008297), Capra hircus PV type 1 (ChPV1; NC_008032), Mastomys coucha PV type 2 (McPV2; DQ664501), Micromys minutus PV (MmPV; NC_008582), Ursus maritimus PV type 1 (UmPV1; NC_010739), Sus scrofa PV type 1a (SsPV1a; EF395818), Chelonia mydas PV type 1 (CmPV1; EU257705), Caretta caretta PV type 1 (CcaPV1; EU257704), Tursiops truncatus PV type 1 (TtPV1; NC_011109), TtPV2 (NC_008184), TtPV3 (NC_011110), and EHPV (NC_011765). The established PV genera are indicated by their Greek symbols. The scale bar indicates the genetic distance (in nucleotide substitutions per site), and the numbers at the internal nodes represent the bootstrap probability percentages as determined for 10,000 iterations by the neighbor-joining method. Only bootstrap values of 75% or more are shown.