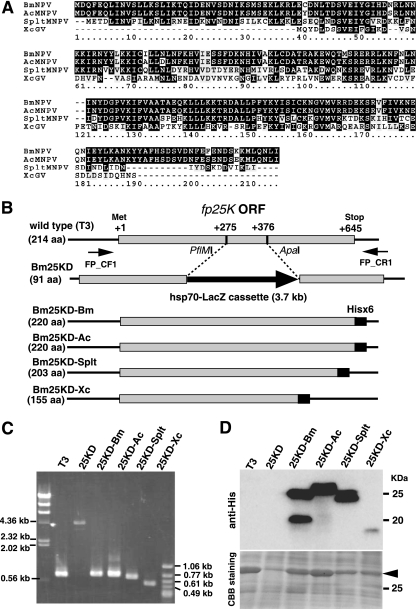
FIG. 1.
Generation of recombinant BmNPVs expressing fp25K genes from BmNPV, AcMNPV, SpltMNPV, and XecnGV. (A) Alignment of FP25K proteins from BmNPV, AcMNPV, SpltMNPV, and XecnGV (XcGV). In the sequences shown, black shading denotes identical residues and gray shading indicates similarities among the four FP25K proteins. (B) Schematic representation of recombinant BmNPVs. The set of PCR primers (FP_CF1 and FP_CR1) used in genotyping experiments is also shown. ORF, open reading frame. (C) PCR analysis of the genomes of T3, Bm25KD (25KD), Bm25KD-Bm (25KD-Bm), Bm25KD-Ac (25KD-Ac), Bm25KD-Splt (25KD-Splt), and Bm25KD-Xc (25KD-Xc). Each genotype was confirmed by PCR using the primers FP_CF1and FP_CR1. (D) Expression of His-tagged FP25K proteins in BmNPV-infected BmN cells. BmN cells were infected with T3 or recombinant BmNPVs, harvested at 3 dpi, and subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-His antibody. The gel stained with Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) is shown in the lower panel. The molecular masses of protein standards are indicated to the right. The arrowhead indicates polyhedrin.