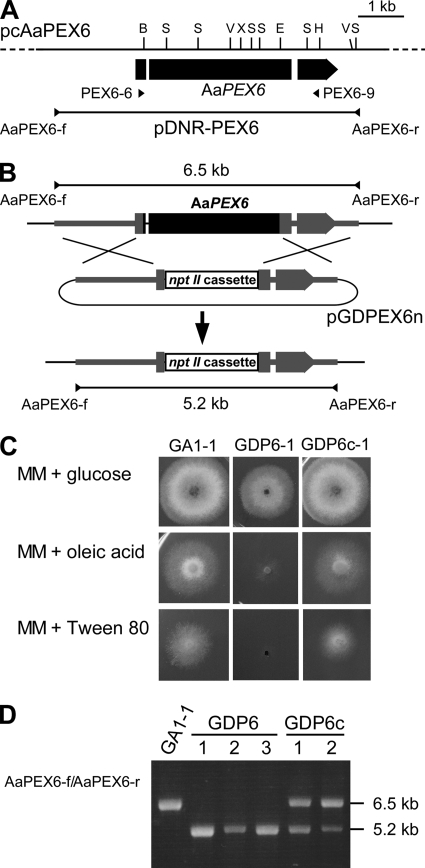
Fig. 5.
Transformation-mediated disruption of AaPEX6. (A) Map of the AaPEX6 locus. The arrowed bar indicates the protein coding region, with introns (white segments), of AaPEX6. Plasmid pDNR-PEX6 contains the entire AaPEX6 region amplified by PCR from cosmid clone pcAaPEX6 DNA using the primer pair AaPEX6-f/AaPEX6-r. Arrowheads (PEX6-6 and PEX6-9) denote the orientations and locations of the oligonucleotide primers used in reverse transcription-PCR experiments. B, BamHI; E, EcoRI; V, EcoRV; H, HindIII; S, SalI; X, XhoI. (B) Structure of the AaPEX6 locus before and after homologous integration of the targeting vector pGDPEX6n. To make pGDPEX6n, a 3.2-kb BamHI-EcoRI fragment within AaPEX6 was replaced with a 1.9-kb BamHI-EcoRI fragment of the nptII cassette. (C) Growth of AaPEX6 disruption-containing and complemented transformants on fatty acid medium. Strains were grown for 4 days on MAM supplemented with glucose, oleic acid, or Tween 80 as the sole carbon source. GA1-1, GFP-Akt1-expressing strain; GDP6-1, AaPEX6 disruption-containing transformant made from GA1-1; GDP6c-1, AaPEX6-complemented transformant made from GDP6-1. (D) PCR analysis of AaPEX6 disruption-containing and complemented transformants. The total DNA of each strain was used as the template for a PCR with the primer pair AaPEX6-f/AaPEX6-r. GDP6-1 to GDP6-3, AaPEX6 disruption-containing transformants; GDP6c-1 and GDP6c-2, AaPEX6-complemented transformants.